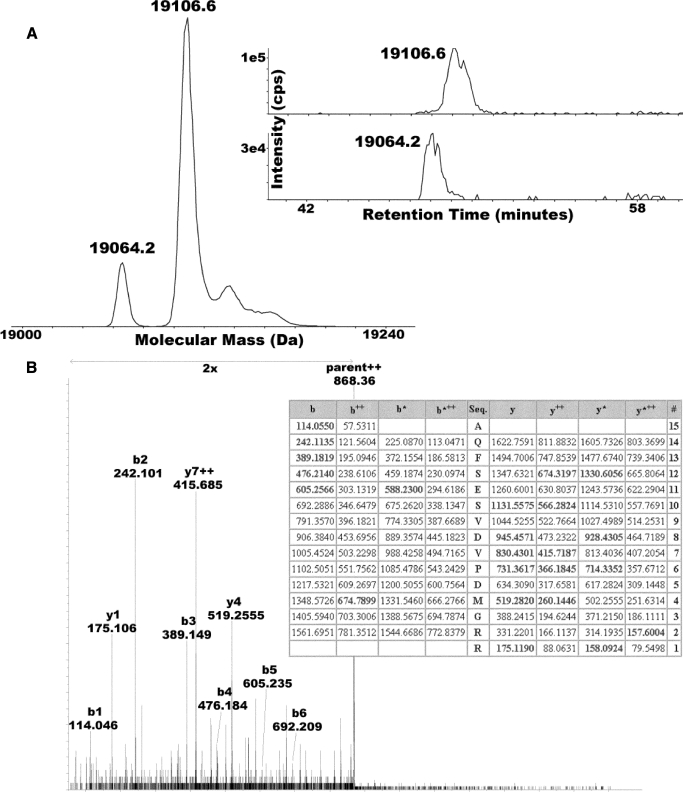
FIGURE 2.
Partial N-terminal acetylation of the Rieske iron-sulfur protein. LC-MS of the cytochrome b6f complex from Nostoc reveals two populations of Rieske ISP. A, electrospray-ionization mass spectrum of Rieske ISP after zero-charge deconvolution reveals sub-populations at 19,064.2 and 19,106.6 Da, consistent with partial acetylation (+42 Da). Specific ion chromatograms for each species are shown in the inset, revealing that the putative acetylated form is more highly retained, consistent with it being more hydrophobic due to having one less charge. B, analysis of an N-terminal tryptic peptide of Rieske ISP by tandem mass spectrometry using collisionally activated dissociation. The collisionally activated dissociation spectrum shown was annotated with respect to the important b-ion series (b1–b5) that are all consistent with N-terminal acetylation. The table was generated by the Mascot algorithm (Matrix Sciences), which picked the N-terminally acetylated N-terminal tryptic peptide of Nostoc Rieske ISP out of the complete protein data base (MSDB at Matrix Sciences on 11/11/08; search run in “no enzyme” mode) as the best match to the experimental dataset with a score of 40 (see Ref. 18). The matched ions are shown in boldface and localize the delta 42-Da modification to the N-terminal amino acid residue.