Figure 1. The Platform Workflow.
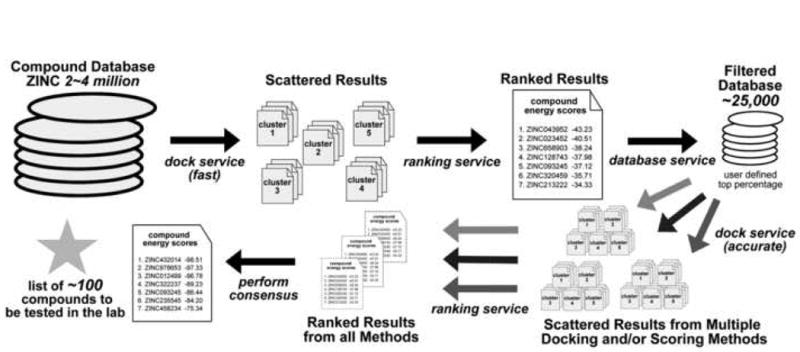
Starting with a large database of compounds, such as the ZINC library, a rapid docking method is used for the initial screening and is distributed via the dock service. Results data, consisting of compound lists ranked from best to worst energy score, are scattered across the grid resources. The ranking service searches for and gathers this data to construct a list of results encompassing the entire database of compounds. From this list, a top percentage of compounds can be selected to make up a new, smaller database of around 25,000 compounds. Conformational data output by the screening for each compound is retrieved by the database service and is used to build this new database. A number of different, more stringent parameters are then used to rescreen these compounds, distributed again by the dock service and results gathered by the ranking service. After performing a consensus amongst all scoring methods, a short list of the best potential binding compounds is generated to test in the lab in vitro.
