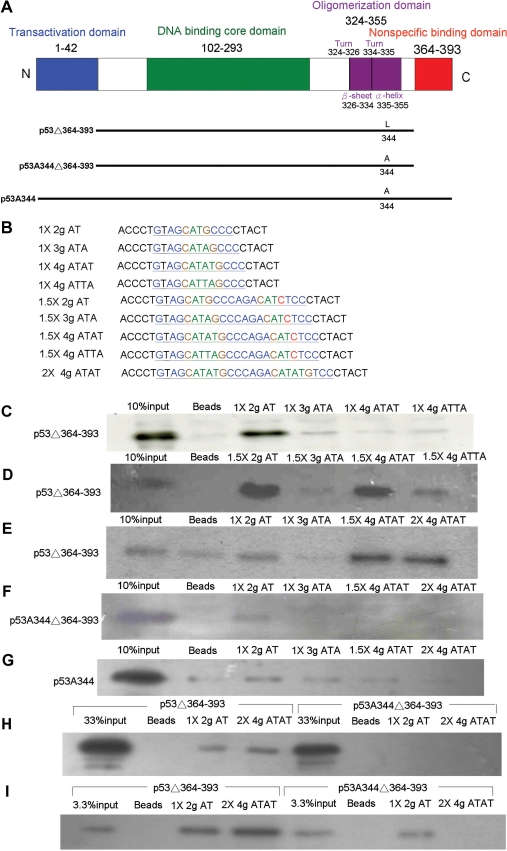
Figure 6.
p53-binding character to various A/T core sequences of p53 response element by DAPA assay (A) Diagrams of the p53 protein structure and oligomerization mutant constructs: There are four major functional domains within 393 amino-acid residues; N-terminal transactivation domain, middle DNA-binding core domain, C-terminal oligomerization and non-specific binding domains. p53Δ364–393: tetrameric form of p53 with non-specific binding domain deletion. p53A344Δ364–393: dimeric form of p53 with non-specific binding domain deletion. p53A344: dimeric form p53. (B) Oligomerization mutants of p53 expression vectors were transfected into H1299 cells. After 48 h incubation, the nuclear proteins were extracted and incubated with various probes in a DAPA assay. Various A/T core sequences with p53 response element designed primers as probes. One hundred micrograms of nuclear extracts were used in C, D, E, F and G; 30 μg of nuclear extracts were used in H; 300 μg of nuclear extracts were used in I. All of the input samples were 10 μg of nuclear extract as 10% loading control in C, D, E, F and G; 33% in H; 3.3% in I. (C) The tetrameric form of p53Δ364–393 can bind to two-base A/T gap CATG core sequences but cannot bind to three-base A/T gap CATAG, four-base A/T gap CATATG, or CATTAG core sequences when the probes as the half site. (D) The tetrameric form of p53Δ364–393 can bind to two-base A/T gap CATG, four-base A/T gap CATATG and CATTAG core sequences but cannot bind to three-base A/T gap CATAG core sequences when the probe was the 1.5-fold half site. Among four-base A/T gap core sequences, the p53-binding affinity in CATATG was higher than CATTAG. (E) The tetrameric form of p53Δ364–393 can bind to four-base A/T gap CATATG core sequences when the probes were the 1.5-fold half site or the 2-fold half site. (F) The dimeric form of p53A344Δ364–393 can bind to the two-base A/T gap CATG core sequence when the probe was the half site but cannot bind to four-base A/T gap CATATG core sequences even with probes as the 1.5-fold half site or 2-fold half site. (G) The other p53 mutant, dimeric form of p53A344, can bind to two-base A/T gap CATG core sequences when the probe as the half site. (H) Tetrameric p53Δ364–393 can bind to two-base A/T gap CATG in a half site or four-base A/T gap CATATG in a 2-fold half site, but dimeric p53A344Δ364–393 can not be detected in all reactions with low nuclear extract samples. (I) Both tetrameric p53Δ364–393 and dimeric p53A344Δ364–393 can bind to two-base A/T gap CATG when the probe was a half site. However, tetrameric p53Δ364–393 can bind to four-base A/T gap CATATG when the probe was a 2-fold half site, but dimeric p53A344Δ364–393 lost it binding affinity at all even reaction with high nuclear extract sample.