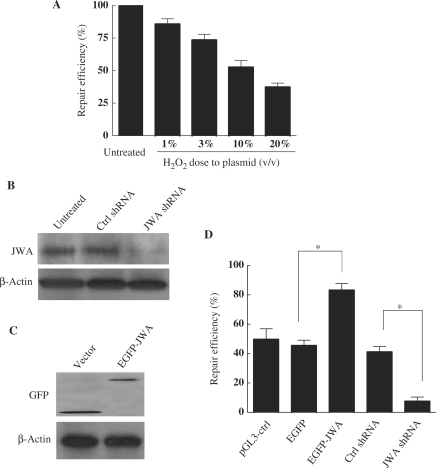
Figure 1.
JWA is required for repairing H2O2-damaged DNA. (A) The repair efficiency of NIH-3T3 cells on damaged plasmid DNA was detected by HCR assay. NIH-3T3 cells were transfected with control LUC plasmid DNA (pGL3-control) or the same plasmid damaged by hydrogen peroxide at concentrations of 1, 3, 10 or 20% (v/v). DNA repair rates were measured as the ratio of LUC activity in extracts from cells transfected with a damaged plasmid to the LUC activity in extracts from cells transfected with an undamaged plasmid. The experiment was done in triplicate. (B) NIH-3T3 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids to knockdown JWA (JWA shRNA), or with the corresponding control vector (Ctrl shRNA), or were left untreated. After 48 h, whole-cell lysates were collected for detection of target proteins by immunoblotting. (C) NIH-3T3 cells were transiently transfected with a plasmid expressing human JWA protein (EGFP-JWA) or a control vector (EGFP-C1). Expression of target proteins 48 h after transfection was examined in whole-cell lysates by immunoblotting. (D) Knockdown of JWA inhibits DRC of damaged plasmids, while overexpression of JWA enhances DRC in NIH-3T3 cells. NIH-3T3 cells were transfected with either the EGFP-C1 control or EGFP-JWA plasmid, control shRNA or JWA shRNA together with undamaged or 10% (v/v) H2O2-damaged LUC plasmids. The pGL3 (undamaged or H2O2-damaged) plamids were transfected as a control for co-transfection efficiency. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the DRC of the damaged LUC reporter was assayed as indicated in (A). The renilla luciferase reporter (internal control, Promega) was used to normalize the activity of the LUC reporter. *P < 0.05.