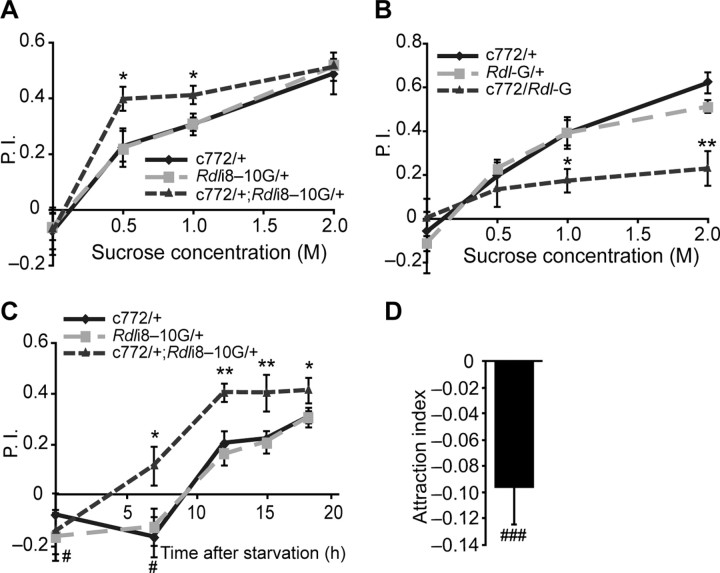
Figure 2.
RDL inhibits appetitive olfactory learning. A, Flies were starved for 18 h and trained using different concentrations of sucrose presented with a 1.5 min exposure to the conditioned odor. Flies carrying the c772-Gal4 driver and the Rdli8–10G transgene exhibited an enhanced performance. B, Flies carrying the c772-Gal4 driver and a UAS-Rdl-G transgene exhibited poor performance in the appetitive learning assay described in (A). C, Flies carrying the c772-Gal4 driver and the Rdli8–10G transgene exhibited an enhanced performance after appetitive olfactory conditioning with 1 m sucrose when starved for 7, 12, 15, and 18 h. The performance scores for all three groups with no starvation and for the two control groups after 7 h starvation were significantly lower than zero. D, Wild-type naive flies without starvation showed a significant avoidance of a T-maze arm that contained 1 m sucrose when given a choice of a second arm without sucrose. Means ± SEM are shown for all panels. For panels A–C, n = 6 for each group under each condition; n = 15 for panel D. A–C, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (Fisher's PLSD); C, D, #p < 0.05; ###p < 0.001 (one-sample Wilcoxon signed-rank test, μ0 = 0).