Abstract
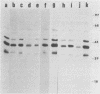
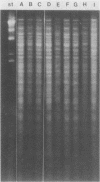
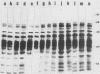
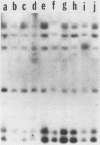
A series of isolates of Streptococcus equi from the United States and Europe were compared by the bactericidal test, immunoblotting, DNA restrictions, and Southern hybridization analysis. All isolates tested were sensitive to the same bactericidal serum. In addition, immunoblotting revealed no differences in M proteins prepared by acid or mutanolysin extraction. Immunoblotting of acid extracts of the isolates with mucosal nasopharyngeal mucus from a convalescent horse revealed the presence of the 41,000- and 46,000-Mr polypeptide fragments of the M protein of S. equi known to be important in stimulating mucosal nasopharyngeal immune responses. DNA restriction analysis of total cell DNA digests, as well as Southern hybridizations using an S. equi M protein gene probe, did not detect any differences among these isolates. Our results, therefore, confirm the antigenic homogeneity of the M proteins of S. equi isolates and suggest that variation in this antigen is not a reason for the failure of commercial vaccines in the field. Interestingly, the protoplast M proteins of all isolates showed remarkable size homogeneity, in contrast to the size variation reported in M proteins of group A streptococci.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini A. M., Hofer M., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. On the formation of spontaneous deletions: the importance of short sequence homologies in the generation of large deletions. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman T. G., Roizman B., Adams G., Stover B. H. Restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of herpes simplex virus DNA: a novel epidemiological tool applied to a nosocomial outbreak. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):488–498. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson E. D., Norcross N. L. The cell surface antigens of Streptococcus equi. Can J Comp Med. 1975 Apr;39(2):110–115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Scott J. R. Size variation of the M protein in group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1384–1401. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galan J. E., Timoney J. F. Mucosal nasopharyngeal immune responses of horses to protein antigens of Streptococcus equi. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):623–628. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.623-628.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Timoney J. F. Molecular analysis of the M protein of Streptococcus equi and cloning and expression of the M protein gene in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3181–3187. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3181-3187.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of type-specific M antigen isolated from a group A, type 1 hemolytic streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):71–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. B., Wilton B. E., Robinson A. J. Identification of Leptospira serovars by restriction-endonuclease analysis. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):163–166. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClenaghan M., Herring A. J., Aitken I. D. Comparison of Chlamydia psittaci isolates by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.384-389.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. J., Ramadass P., Lee A., Marshall R. B. Differentiation of subtypes within Leptospira interrogans serovars Hardjo, Balcanica and Tarassovi, by bacterial restriction-endonuclease DNA analysis (BRENDA). J Med Microbiol. 1982 Aug;15(3):331–338. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-3-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjold S. A., Quie P. G., Fries L. A., Barnham M., Cleary P. P. DNA fingerprinting of Streptococcus zooepidemicus (Lancefield group C) as an aid to epidemiological study. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1145–1150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Moseley S. L., Kingscote B. New method for classification of leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroup pomona by restriction endonuclease analysis: serovar kennewicki. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.585-587.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F., Eggers D. Serum bactericidal responses to Streptococcus equi of horses following infection or vaccination. Equine Vet J. 1985 Jul;17(4):306–310. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1985.tb02505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F., Timoney P. J., Strickland K. L. Lysogeny and the immunologically reactive proteins of Streptococcus equi. Vet Rec. 1984 Aug 18;115(7):148–149. doi: 10.1136/vr.115.7.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F., Trachman J. Immunologically reactive proteins of Streptococcus equi. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.29-34.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock J. B. Purification and antigenicity of an M-like protein of Streptococcus equi. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.116-122.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]