Fig. 3.
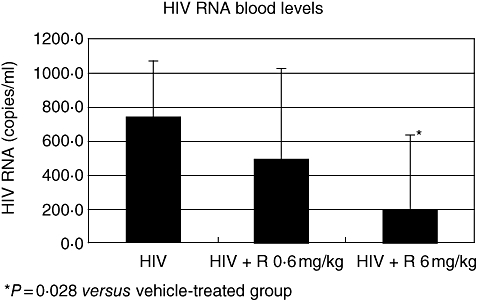
The effects of rapamycin (RAPA) on co-cultivation assays of spleen cells collected from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected human peripheral blood leucocytes (hu-PBL)-SCID mice. Cells were recovered from the spleens of hu-PBL-reconstituted and HIV-infected mice treated with either RAPA (0·6 versus 6 mg/kg) or its vehicle alone. Spleen cells (105) were co-cultured with 105 human allogeneic T cells which were activated preventively with 5 µg/ml phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and cultivated in the presence of 50 U/ml interleukin-2. Virus replication was determined after 10 days of culture by detection of p24 gag antigen in culture supernatant using a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. *P = 0·021 versus the vehicle-treated control. Each group consisted of eight mice.
