Figure 2. The individual K/R or K/Q substitutions do not affect the overall acetylation level of hsp90 but affect the ability of hsp90α to bind ATP, co-chaperones and client proteins.
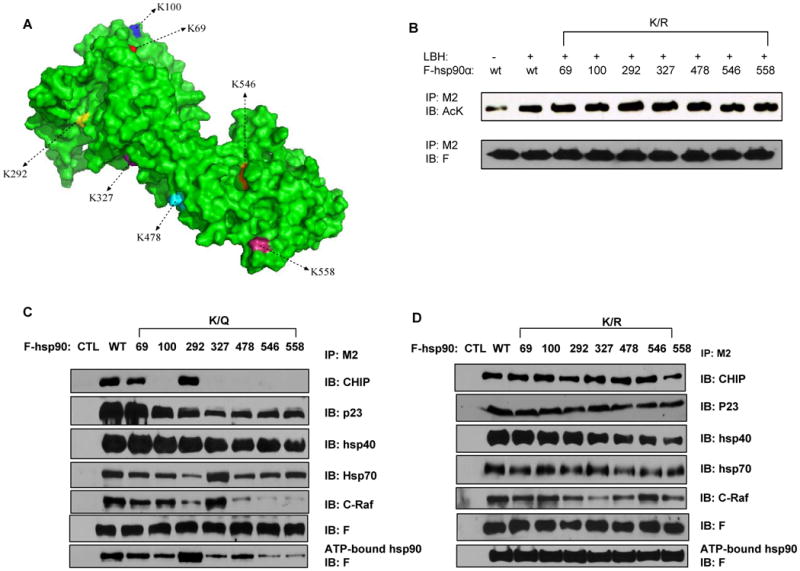
(A) The space-filling molecular structure model of hsp90. The seven lysine residues are shown in different colors. (B) Transfectants of F-hsp90α, with or without K/R substitutions, were treated with or without 100 nM of LBH. Following this, immunoprecipitates with M2 antibody were immunoblotted with either anti-AcK or anti-F antibody. (C, D) Transfectants of F-hsp90α with K/Q (C) but not K/R substitutions (D) affect ATP binding of hsp90α. Precipitates from the mixture of cell lysates containing hsp90α and ATP-sepharose were analyzed with anti-F antibody. Also, following transfections of F-hsp90α, with or without K/Q or K/R substitutions, immunoprecipitates with M2 antibody were immunoblotted with anti-CHIP, anti-p23, anti-hsp40, anti-hsp70, anti-c-Raf or anti-F antibody.
