Figure 5. Acetylation of hsp90α promotes in vitro invasion by breast cancer cells.
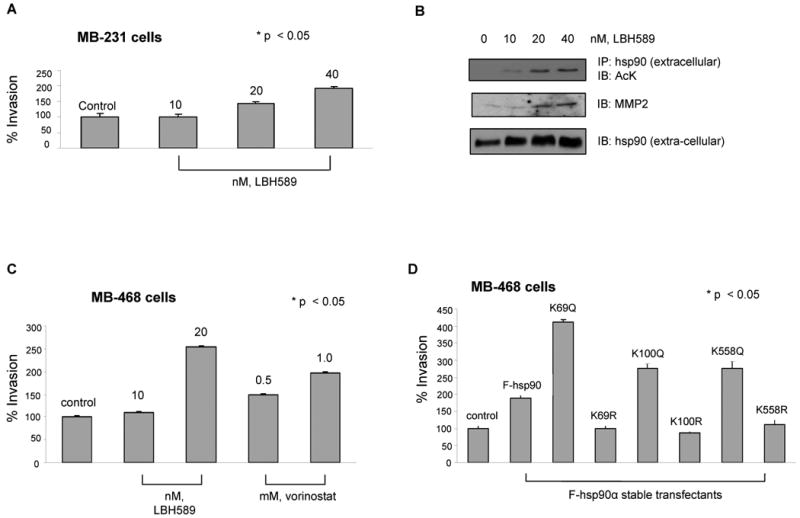
(A and B) LBH promotes in vitro invasion of MB-231 cells, associated with extra-cellular location and binding of acetylated hsp90α to MMP-2. (A) MB-231 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of LBH589 for 16 hours. Following this, an aliquot of the cells was used for determining in vitro matrigel invasion (see text for details) Columns, average results of three independent experiments; bars, SD. *, p < 0.05. (B) Alternatively, supernatant of serum starved LBH treated MDA-MB-231 cells were concentrated and immunoprecipitates with anti-hsp90α antibody were immunoblotted with anti-AcK, anti-MMP-2 or hsp90α antibody. (C) HDAC inhibitors promote in vitro invasion by MB-468 breast cancer cells. Serum-starved MB-468 cells were used for determining in vitro matrigel invasion in the indicated concentrations of LBH589 or vorinostat and then evaluated for in vitro invasion. Columns, average results of three independent experiments; bars, SD. *, p < 0.05. (D) Stable transfection of K/Q but not K/R substituted mutants promote in vitro invasion by MB-468 cells. Serum-starved MB-468 cells expressing either F-hsp90α, or K/Q or K/R substituted mutants were used for determining in vitro matrigel invasion. Columns, average results of three independent experiments; bars, SD. *, p < 0.05.
