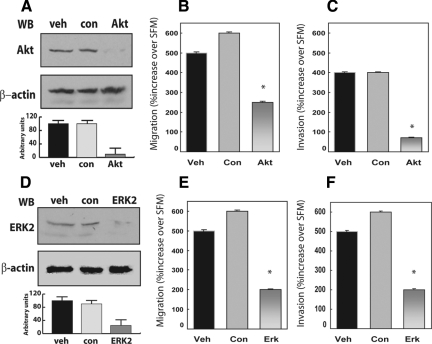
Figure 4.
Depletion of endogenous Akt and ERK1/2 proteins effectively reduces proepithelin-mediated migration and invasion of DU145 cells. Gene knockdown for Akt and ERK1/2 was achieved by siRNA. Twenty-four hours after transfection, DU145 cells were serum-starved for 24 hours and then stimulated with 240 nmol/L of purified proepithelin. After 24 hours, cells were processed and analyzed for migration (B and E) and invasion (C and F). Values are expressed as percent increase over SFM (70 ± SD). *P < 0.05 compared with vehicle-treated control cells (first column). The level of endogenous Akt (A) and ERK1/2 proteins (D) was detected by immunoblot using anti-ERK1/2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) or anti-Akt polyclonal antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology). Protein loading was normalized using anti-β-actin polyclonal antibodies (Sigma-Aldrich). One representative blot is shown. Densitometric analysis of the Akt and ERKs protein levels (A and D) was performed using the Image J program (National Institutes of Health). Values in arbitrary units from three independent experiments are shown.