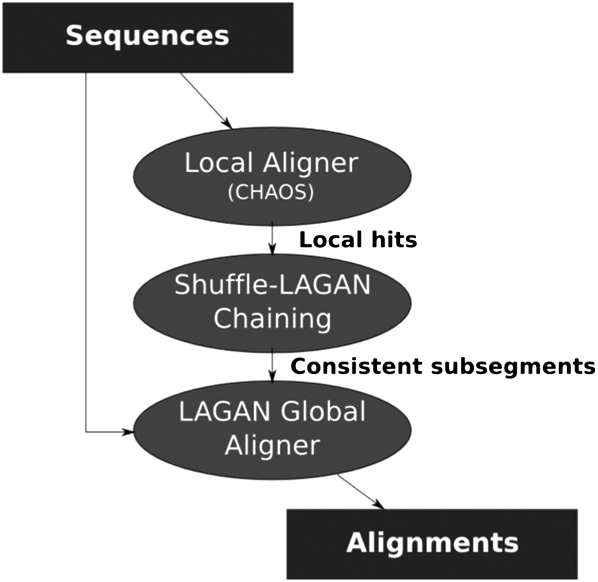
Figure 1.
Overview of the Shuffle-LAGAN algorithm. S-LAGAN first locates all local areas of similarity between the two sequences using a local alignment algorithm. A subset of these is selected using the 1-monotonic chaining algorithm (Fig. 2). Finally, global alignments are built (using LAGAN) for consistent subsegments of the 1-monotonic chain (areas without rearrangements). The S-LAGAN algorithm is not symmetric, requiring two alignments to identify all duplications.