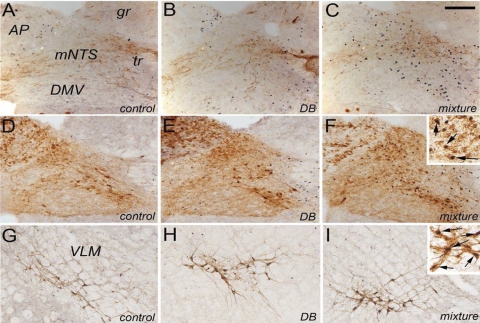
Fig. 1.
Representative color photomicrographs depicting dual immunolabeling for Fos (black nuclear label) and either calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP; A–C) or dopamine β-hydroxylase (DβH; D–F) (brown cytoplasmic label) within the medial caudal visceral nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) and Fos + DβH immunolabeling within the ventrolateral medulla (VLM) (G–I) in rats after gavage of water (control), denatonium benzoate (DB) alone, or a mixture of bitter taste receptor (T2R) ligands (mixture). Neuronal Fos labeling within the area postrema (AP), caudal visceral NTS, and VLM appeared greatest in rats gavaged intragastrically with the T2R agonist mixture. Quantitative data are provided in Figs. 2 and 3 and in Table 1. Insets in F and I provide higher-magnification views of double-labeled (i.e., Fos-positive noradrenergic) neurons (arrows). DMV, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus; gr, gracile nucleus; mNTS, medial subnucleus of the solitary tract; tr, tractus solitarius. Scale bar = 100 μm, A–I.