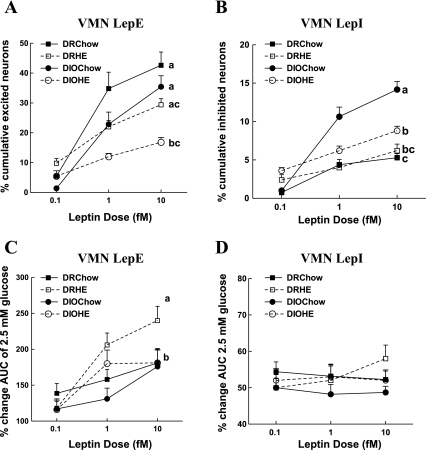
Fig. 2.
Effects of genotype and maternal diet on leptin-induced changes in [Ca2+]i oscillations. VMN neurons of offspring of diet-resistant (DR; n = 8) and diet-induced obesity (DIO; n = 8) dams fed chow, and DR (n = 5) and DIO (n = 5) dams fed high-energy (HE) diet during gestation and lactation were exposed to increasing doses of leptin (0.1, 1.0, and 10 fM). Total numbers of neurons analyzed for a given group are as follows: DR chow = 286, DR HE = 429, DIO chow = 292, DIO HE = 405. A: cumulative percentage of LepE neurons at the three increasing leptin doses. B: cumulative percentage of LepI neurons at the three increasing leptin doses. C: percent increase in AUC on the addition of increasing doses of leptin compared with 2.5 mM glucose. D: percent decrease in AUC on addition of leptin compared with 2.5 mM glucose. Data are expressed as means ± SE. Parameters with differing superscripts differ from each other by P < 0.05 by post hoc Bonferroni tests after intergroup differences were found by ANOVA.