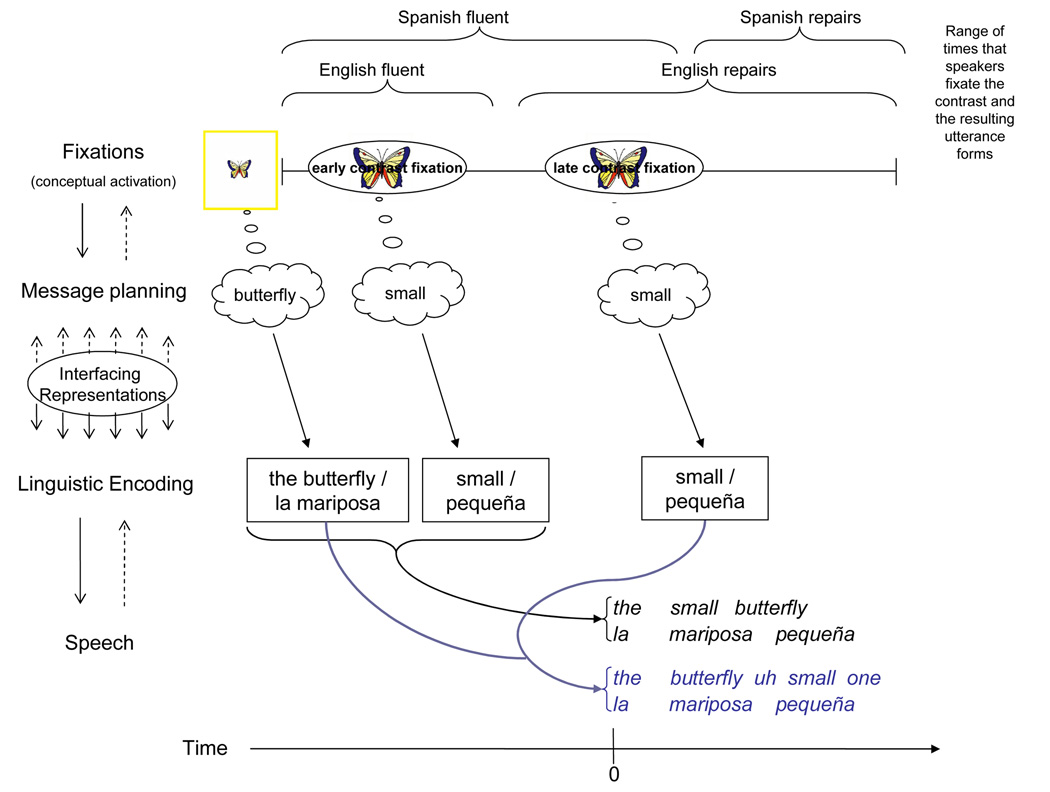
Figure 4.
Schematic of the proposed lexically-incremental message-to-utterance planning interface for picture descriptions in English and Spanish. Arrows represent proposed connections (dotted arrows represent feedback connections). Time=0 is NP onset. The process begins with an initial fixation to the target (small butterfly), followed by a fixation to the size-contrast (large butterfly). When the contrast is fixated early, the resulting expression is fluent in both languages. When the contrast is fixated just after NP onset, the result is a fluent expression in Spanish, and a disfluent repair in English (see Figure 3; the modal first contrast fixation for both expression types is immediately following NP onset).