Fig. 5.
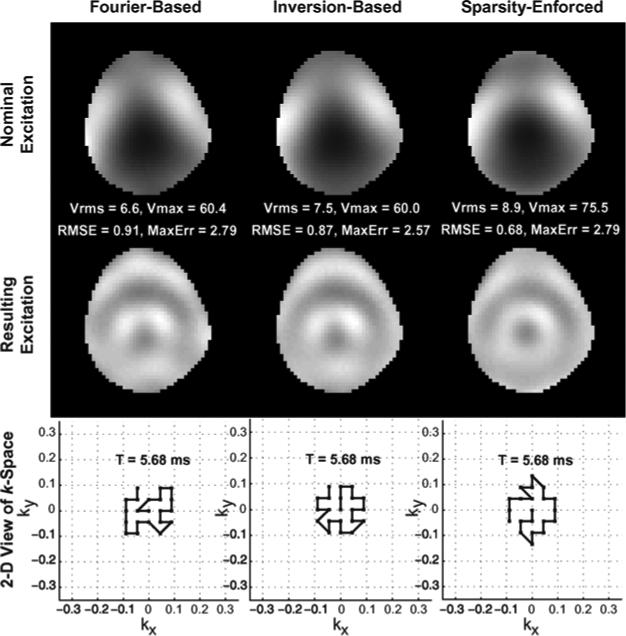
Bloch-simulated 21-spoke pulses designed by the Fourier, inversion, and sparsity-enforced spoke placement algorithms for mitigating B1 inhomogeneity in the head-shaped water phantom at 7 T. Columns, from left to right: results of the Fourier, inversion, and sparsity-enforced methods. Top row: excitations produced by each algorithm. Middle row: magnetizations after accounting for the inhomogeneity. Bottom row: 2-D view of k-space illustrating each spoke placement; each trajectory ends at the center of k-space. The sparsity-enforced pulse produces the lowest-RMSE excitation.
