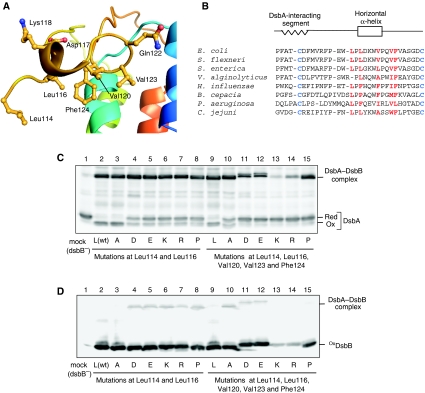
Figure 6.
Functional role of the DsbB horizontal helix in DsbA oxidation. (A) Close-up view of the horizontal helix of DsbB(Cys41Ser) in complex with Fab. Leu114, Leu116, Val120, Val123 and Phe124 located on the membrane-facing side and Asp117, Lys118 and Gln122 located on the aqueous side are represented by ball and stick. (B) Sequence alignment of DsbB orthologues for the region from Pro100 to Cys130. Conserved essential cysteines in the P2 loop are in blue. Residues in red denote membrane-facing hydrophobic residues near or inside the horizontal helix (see (A)). (C) In vivo redox state of DsbA in cells expressing each DsbB variant, in which Leu114 and Leu116 (plus Val120, Val123 and Phe124) are simultaneously replaced with alanine (A), aspartate (D), glutamate (E), lysine (K), arginine (R) or proline (P). Reduced and oxidized forms of DsbA were separated by 12.5% SDS–PAGE after cysteine alkylation with AMS and detected by western blot analysis with an anti-DsbA antibody. (D) In vivo redox states of the indicated DsbB variants, which were detected by western blot analysis (12.5%) with an anti-myc antibody.