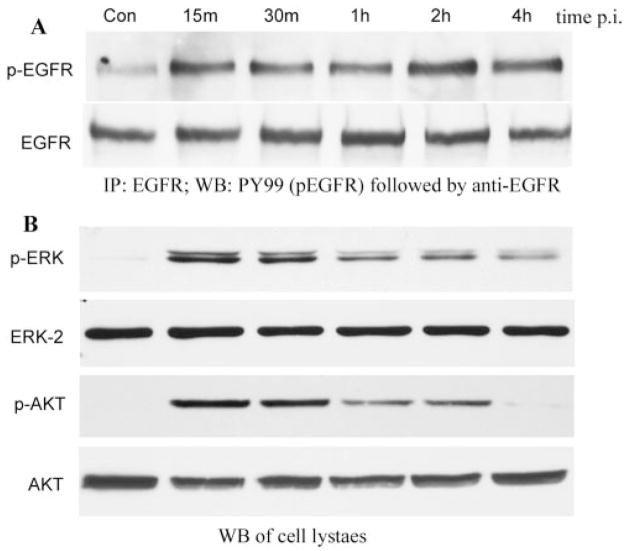
FIGURE 1.
P. aeruginosa–induced EGFR, ERK1/2, and Akt phosphorylation. HUCL cells were grown to ~90% confluence on 100-mm plates and serum-starved overnight. Cells were then infected with P. aeruginosa at a cell-to-bacterium ratio of 1:25 over a 4-hour time course. Cell lysates were prepared at the designated time points PI. (A) For immunoprecipitation, 800 μg protein for each sample was immunoprecipitated (IP) with 2.5 μg agarose-conjugated EGFR antibodies, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and probed (WB) with mouse anti-PY99 antibody (top); after stripping, reproved with mouse anti-EGFR (bottom). (B) To assess phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Akt, 10 and 30 μg cell lysates of the same samples were subjected to Western blot analysis (WB) with either anti-phospho-ERK1/2 (pERK) or anti-phospho-Akt (pAKT). To normalize protein loading onto blots, anti-ERK2 (ERK2), and anti-Akt (AKT) antibodies were used as probes. The results are representative of three independent experiments.