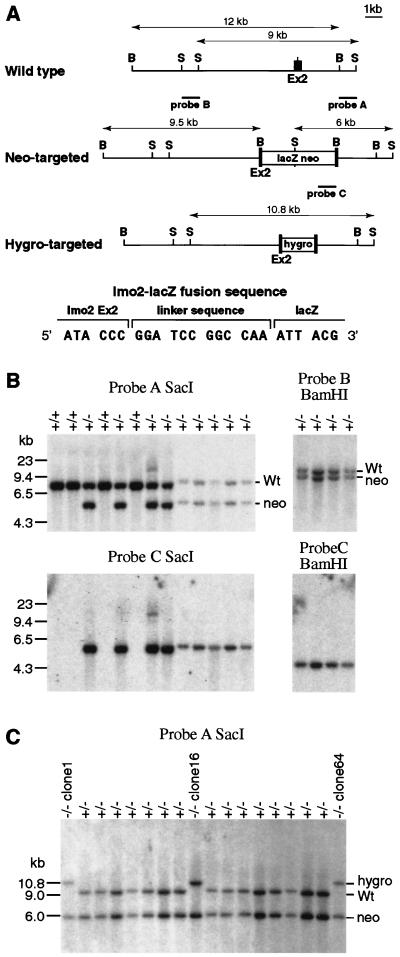
Figure 1.
Lmo2–lacZ fusion gene knock-in by homologous recombination. Two constructs were used to create the Lmo2-targeted ES cells used in this study. CCB ES cells were transfected with pKO5-lacZ-neo (A), and targeted events were detected by filter hybridization. Several targeted clones were initially analyzed, and one (designated KZ26) was chosen based on its ability to yield consistently high levels of chimerism in mice after injection into blastocysts. The KZ26 clone +/− was used for a second transfection with pKO5hygro(tk), and three clones (clones 1, 16, and 64) were studied in which the second allele of Lmo2 had been targeted to yield KZ26 −/− (Lmo2 −/−) ES cells. (A) Construction of the Lmo2–lacZ fusion gene targeting vector was done by cloning of 4.5-kilobase (kb) blunt-ended SfiI fragment of SfiI-lacZ-MC1neopA (38) into a blunt-ended BamHI site of gene targeting vector pKO5(tk) (14). In the resulting clone, KO5-lacZ-neo, the 24th codon of Lmo2 (exon 2) was linked to the 2nd codon of lacZ by a 12-bp linker sequence. The hygromycin-targeting vector pKO5hygro(tk) and the probes used to assess gene targeting, indicated on the map of pKO5-lacZ-neo, have been described (14). The targeting of the pKO5-lacZ-neo into Lmo2 yields a 6-kb SacI fragment with probe A (compared with a 9-kb germ-line band) and a 9.5-kb BamHI band with probe B (compared with a 12-kb germ-line band). Probe C is a neo probe used to verify a single insertion of the targeting vector. Targeting of pKO5hygro(tk) into Lmo2 yields a 10.8-kb SacI band with probe A and a 13.8-kb BamHI band with probe B. S, SacI; B, BamHI. (B) Detection of homologous recombination in ES clone DNA by Southern filter hybridization with probe A (3′ flanking), probe B (5′ flanking), and probe C (internal). Hybridization of representative +/+ (wild-type) and +/− (neo-targeted) clones is shown. Wt, wild-type hybridization band. (C) Identification of three independent double-targeted Lmo2 −/− clones (clones 1, 16, and 64) by filter hybridization with probe A. The integrity of these second targeted alleles was verified by using probe B and an internal hygromycin probe (data not shown).