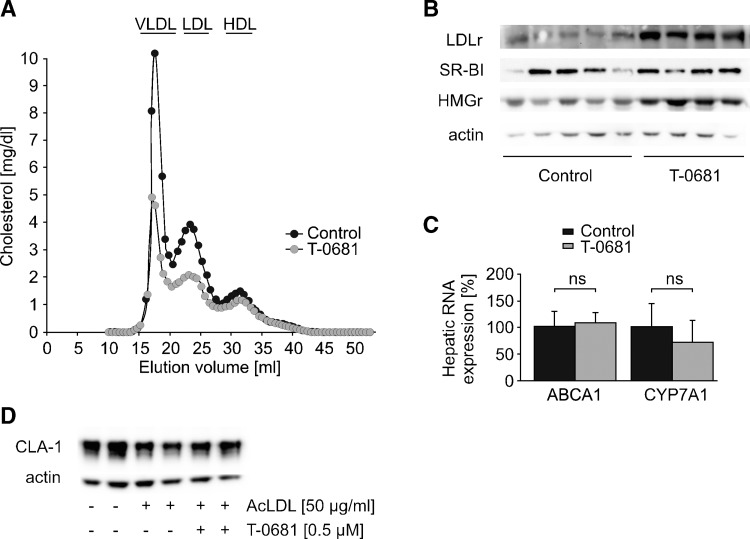
Fig. 2.
Regulation of hepatic proteins involved in cholesterol homeostasis. To differentiate whether T-0681 directly influences certain proteins involved in cholesterol homeostasis or whether regulation of such hepatic proteins is secondary to cellular cholesterol depletion, a short-term in vivo study and in vitro studies were performed. A–C: Short-term study (10 days), in which NZW rabbits on a 0.2% cholesterol diet were treated with T-0681 (36 nmoles/kg/day) or a respective control. At study termination, plasma of each group (n = 4–5) was pooled and subjected to FPLC analysis (A). B: Western blot analysis showing hepatic expression of LDLr, SR-BI, and HMG-CoA reductase (HMGr); each lane shows the protein expression of an individual rabbit. Actin served as loading control. C: Real-time PCR measurement of hepatic ABCA1 and CYP7A1 RNA levels; ns, nonsignificant (n = 4–5). D: Western blot showing human SR-BI (CLA-1) expression in normal HepG2 cells and in HepG2 cells loaded with AcLDL and subsequently incubated with vehicle or T-0681. This representative experiment was run in duplicate, and actin served as loading control.