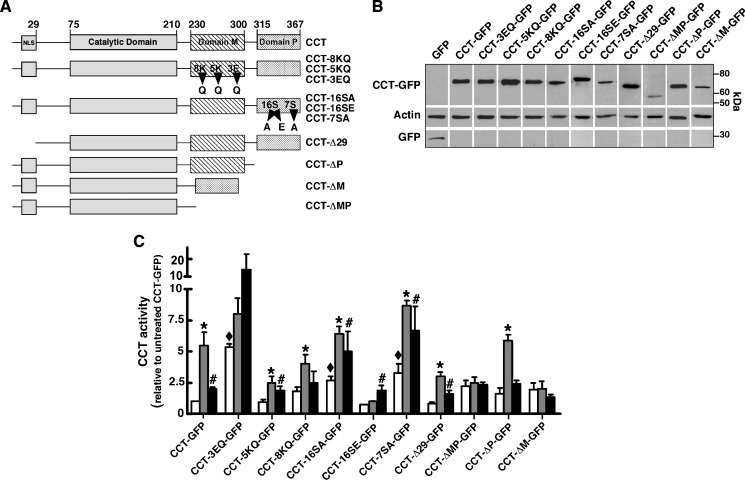
Fig. 2.
In vitro activity and expression of CCT-GFP mutants. A: Domain structure of wild-type and CCTα mutants. GFP was fused to the C terminus of all constructs (not shown). B: CHO58 cells were transfected with CCT-GFP or the indicated mutants at 37°C for 12–14 h, shifted to 40°C or 42°C for 2 h and harvested, and 16,000 g supernatants were prepared and immunoblotted for GFP and actin. C: Enzyme activity was assayed in cell supernatants in the absence of lipid activators (open bars), with phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho)-oleate vesicles (1:1, mol/mol) (grey bars), or with PtdCho-FOH vesicle (3:2, mol/mol) (black bars) as described in Materials and Methods. Background CCT activity in supernatants from cells transfected with pEGFP was subtracted. Activity of wild-type and CCT mutants was normalized to expression of individual CCT-GFP proteins (measured by immunoblotting) and then expressed relative to activity under unstimulated conditions. CCT activity averaged 1,288, 1,091, and 1,217 dpm/assay in the supernatants of pEGFP-transfected cells without addition, plus oleate, or plus FOH, respectively. Activity averaged 1,653, 7,138, and 4,124 dpm/assay in supernatants from CCT-GFP-expressing cells with no addition, plus oleate, or plus FOH, respectively. Results are the mean and SEM of three separate experiments. *P < 0.05 compared with corresponding unstimulated activity; #P < 0.05 compared with corresponding unstimulated activity; ♦P < 0.05 compared with unstimulated CCT-GFP.