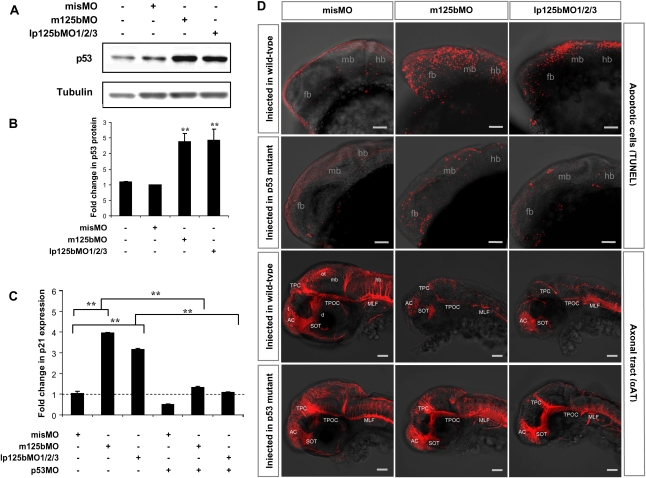
Figure 6.
Loss of miR-125b elevates p53 and triggers p53-dependent apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. (A) Elevation of p53 protein caused by loss of miR-125b in zebrafish embryos: Embryos were injected with misMO, m125bMO, or lp125bMO1/2/3. Western blotting was performed at 24 hpf. (B) The p53 protein level was quantified from the Western blot bands in A, normalized to tubulin level, and presented as fold change ± SEM (n ≥ 3) relative to the p53 level in the misMO-injected embryos. Two-tail t-test results are indicated by (**) P < 0.01, relative to the misMO-injected control. (C) qRT–PCR of p21 transcripts at 24 hpf in embryos injected with different combinations of morpholinos. p53MO indicates a morpholino blocking translation of p53. The values were normalized to the expression level of β-actin and represented as average fold change ± SEM (n ≥ 4) relative to the expression level in misMO-injected embryos (dashed line). Two-tail t-test results are indicated as (**) P < 0.01. (D) TUNEL assay for detecting apoptotic cells (visualized as red spots) in the 24-hpf brains and acetylated tubulin staining (αAT) marking mature neurons and axonal tracts in the 48-hpf brains of wild-type and p53M214K mutant embryos microinjected with misMO, m125bMO, or lp125bMO1/2/3. Each image is a projection of multiple optical slides obtained from a representative embryo. Three embryos were observed for each condition for the TUNEL assay, and five were observed for each condition in the αAT staining. All of them had a similar phenotype as the representative images. (AC) Anterior commissure; (d) diencephalon; (fb) forebrain; (hb) hindbrain; (mb) midbrain; (MLF) medial longitudinal fasciculus; (ot) optic tectum; (SOT) supraoptic tract; (TPC) tract of posterior commissure; (TPOC) tract of postoptic commissure; (t) telencephalon. Bar, 50 μm.