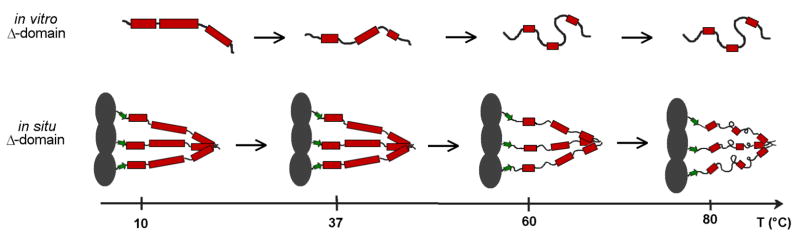
Figure 6.
A comparison of thermally induced perturbations to Δ-domain secondary structure in vitro (top) and in situ (bottom). The models incorporate results of the Raman amide I band analyses and the sizes of the cooperative units (〈nc〉) determined from sedimentation and thermodynamic data (see text). A key feature is that at physiological temperature (37 °C) the structural organization of the in situ Δ-domain is greater than that of the in vitro Δ-domain. In particular, each chain of the in situ trimer retains full α-helicity, whereas the in vitro monomer is partially unfolded.