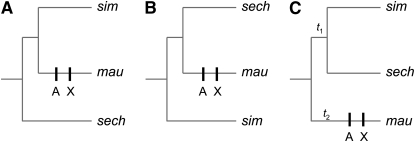
Figure 5.—
Inferring the evolutionary history of the substitutions causing the hlx-Su(hlx) hybrid incompatibility. (A) Assuming genealogical histories with either D. sechellia (sech) or (B) D. simulans (sim) as outgroup species, the most parsimonious histories have the causative substitutions at hlx and Su(hlx) derived in the D. mauritiana (mau) lineage. X, X-linked hlx substitution; A, autosomal Su(hlx) substitution. (C) Assuming a genealogical history with D. mauritiana as the outgroup species, the causative substitutions at hlx and Su(hlx) could be derived in D. mauritiana (t1) or in the common ancestor of the D. simulans–D. sechellia (t2); however, given the disparity in branch lengths (t2 ≪ t1), there has been more time for hlx and Su(hlx) to evolve along the external branch leading to D. mauritiana than the very short internal branch of the D. simulans–D. sechellia common ancestor. The functionally derived hlxmau allele therefore appears to be incompatible with functionally ancestral Su(hlx) alleles from D. sechellia and D. simulans.