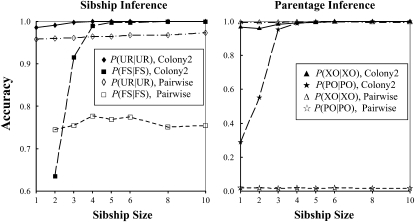
Figure 2.—
Accuracy of parentage and sibship inferences as a function of full sibship size. A simulated data set contains a number of f full-sib families, each having a number of n offspring (sibship size). The total size of the offspring sample is nf = 120. A simulated data set also contains a candidate father sample consisting of on average f/2 fathers and 100 − f/2 unrelated males. Candidate mothers are assumed unavailable. All sampled individuals are genotyped at four loci, each having 10 codominant alleles of an equal frequency. The data sets are comparatively analyzed by our likelihood method and the pairwise likelihood method, denoted as “Colony2” and “Pairwise,” respectively. Inference accuracy is measured by P(FS | FS) and P(UR | UR) for sibship and by P(PO | PO) and P(XO | XO) for parentage.