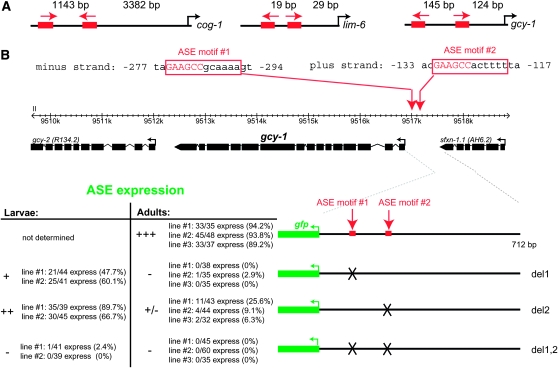
Figure 5.—
gcy-1 expression also depends on two ASE motifs. (A) Schematic of the location of the functional ASE motif in the cog-1 (Figure 3), lim-6 (Etchberger et al. 2007, 2009), and gcy-1 (B) loci. Spacings in between the 6-bp core (binding site for zinc fingers 3 and 4 of CHE-1) and translational start sites are shown. Arrows indicate the orientation of motifs. Note that we have previously documented a large number of cis-regulatory modules that drive expression in ASE and contain only a single ASE motif (e.g., gcy-5, gcy-7, lsy-6, etc.) and that completely isolated ASE motifs are sufficient to drive expression in the ASE neurons (Etchberger et al. 2007, 2009). (B) Reporter gene analysis of the gcy-1 locus. All constructs were generated by PCR fusion and scored in a otIs151 transgene background to allow identification of the ASE neurons. Mutations are complete deletions of the 12-bp site. The importance of individual ASE motifs is different, which is reminiscent of the cog-1 case, but not as drastic.