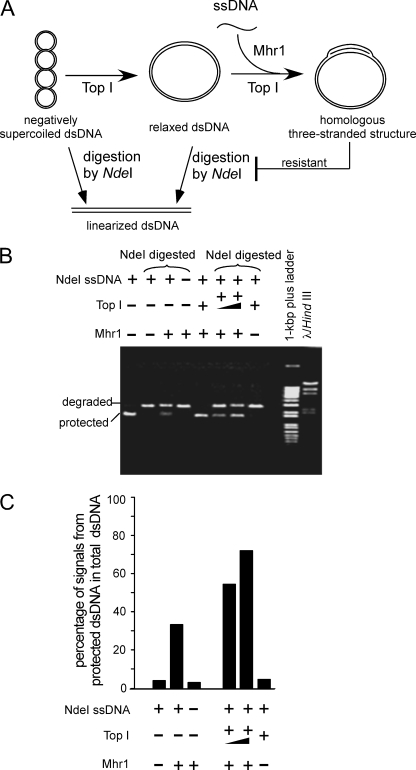
FIGURE 4.
Preferential Mhr1-catalyzed homologous three-stranded structure formation in the presence of eukaryotic topoisomerase I. A, schematic diagrams of the formation of homologous three-stranded structures by Mhr1 with relaxed cc-dsDNA and the ssDNA oligonucleotide in the presence of calf thymus topoisomerase I. B, Mhr1-catalyzed homologous three-stranded structure formation. Negatively supercoiled pUC18 cc-dsDNA was relaxed by the treatment with calf thymus topoisomerase I (Top I). To initiate Mhr1-catalyzed homologous pairing, the relaxed pUC18 cc-dsDNA and active calf thymus topoisomerase I were added to the reaction mixture containing the Mhr1-NdeI ssDNA oligonucleotide complexes. Relaxed pUC18 cc-dsDNA (41.8 μm) was incubated with 1.3 μm NdeI ssDNA oligonucleotide, Mhr1 (0 and 3.9 μm) and calf thymus topoisomerase I at 37 °C for 30 min. As controls, untreated negatively supercoiled pUC18 cc-dsDNA (41.8 μm) was incubated with 1.3 μm NdeI ssDNA oligonucleotide and Mhr1 (0 or 3.9 μm) (without calf thymus topoisomerase I) at 37 °C for 30 min. After the incubation, the DNA products were digested with NdeI, the proteins were removed by SDS and proteinase K treatments, and the products were analyzed by gel electrophoresis, as described in the legend to Fig. 3B. Note that for the topoisomerase-minus control (Top1-), no calf thymus topoisomerase I was added during the entire experimental process. C, a quantitative representation of the results shown in B. The DNA species were detected by a Southern blot analysis, and the percentages of the signals derived from the NdeI-resistant dsDNA among those from the total dsDNA are plotted, as described in the legend to Fig. 3C.