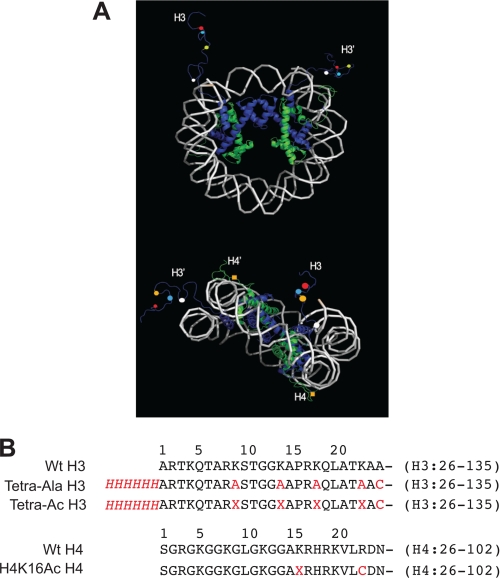
FIGURE 2.
Potential nucleosome sites recognized by the Gcn5 bromodomain. A, the relative orientation of the H3 and H4 histone tails and potential histone acetylation sites based on mononucleosome structure 1KX5 (32). Mononucleosome DNA is depicted in white. H3 and H3′ histones are shown in blue, and H4 and H4′ histones are in green. The histones H2A and H2B are omitted for clarity. In the top image, the mononucleosome is oriented to emphasize the positions of the two H3 tails. The four potential acetylation sites lysine 9 (red), lysine 14 (green), lysine 18 (yellow), and lysine 23 (white) are labeled as colored balls. In the bottom image, the mononucleosome is oriented to emphasize the relative positions of H3 tails and H4 tails. The lysine 16 residues on both H4 tails are labeled as yellow squares. B, the amino acid sequences of the histones used in this study. Deviations from unmodified, wild-type sequences are shown in red. The His6 affinity tag is denoted in red and italicized. Lysine residues that are acetylated on their side chain amine are denoted as X.