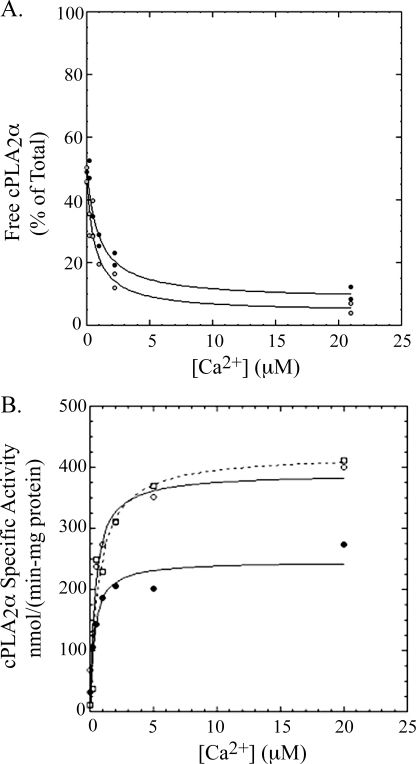
FIGURE 9.
A, binding of cPLA2α-PAP and cPLA2αS505P to PAPC vesicles. Binding solutions contained 1 ml of buffer A, 0.5 mg/ml BSA, and 200 μm PAPC as vesicles and 50 ng of cPLA2α-PAP (filled circles) or cPLA2αS505P (open circles). After ultracentrifugation, two 100-ml aliquots of the supernatant were each submitted to the standard radiometric cPLA2α assay to determine the amount of enzyme not bound to vesicles. The latter is plotted as the percentage of enzyme added to each binding solution, where 100% corresponds to the radiometric assay signal measured for 5 ng of cPLA2α added directly from the stock solution to the radiometric assay mixture (see “Experimental Procedures”). Each experimental condition was carried out in duplicate, and both data points are plotted. B, hydrolysis of [14C]PAPC vesicles by cPLA2α-PAP, cPLA2αS505P, and cPLA2αS505P/S727P versus the concentration of calcium. Reactions contained 0.1 ml of buffer A, 0.5 mg/ml BSA, and 200 μm [14C]PAPC as vesicles and 200 ng of cPLA2α-PAP (filled circles, solid line) or cPLA2αS505P (open circles, solid line) or cPLA2αS505P/S727P (open squares, dashed line). Reactions were quenched after 2 min at 37 °C. Each experimental condition was carried out in duplicate, and both data points are plotted.