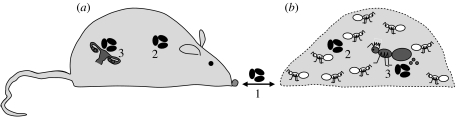
Figure 2.
(a) Steps of infection and anti-parasite defence of individual organisms and (b) insect societies. (1) Border defence: parasites (black ovals) are prevented from entering the body or colony by avoidance behaviour and consolidated physiological defences in the epithelia or at nest entrances. (2) Soma defence: immune defence acts to prevent infection of somatic tissue (cells in the body and sterile workers in insect colonies). (3) Germ line and offspring defence: the reproductive tissue (ovaries) of organisms and the reproductive individuals (queens) of insect colonies are subject to specific immune privileges to prevent offspring infection.