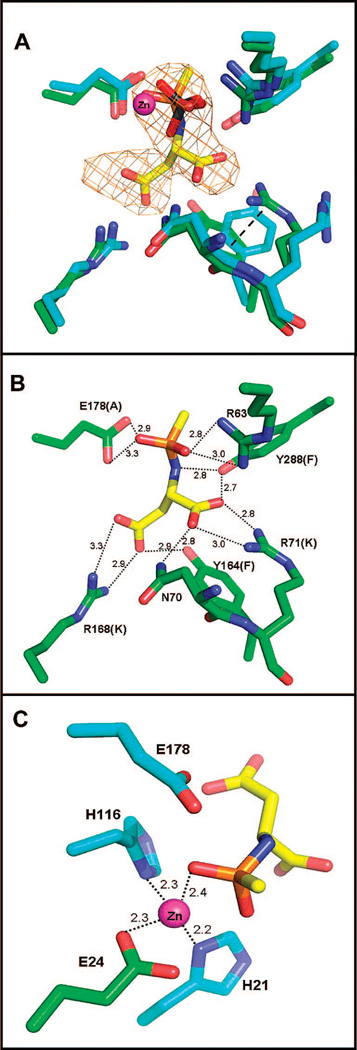
Figure 4.
(A) Overlay of the active sites of the apoenzyme (blue gray) and the intermediate analogue complex (green) structures. The catalytic zinc is colored magenta, and the phosphate molecule from the apo structure (light orange representing the phosphorus atom) is located 0.7 Å from the position of the phosphonate group of the catalytic intermediate analogue in the complex structure. Well-defined difference density (omit Fo – Fc map, contoured at 3σ) allows accurate positioning of the intermediate analogue into the active site. There are only minor changes in the positions of the substrate binding groups, except for the conformational rearrangements of the side chains of R71 and Y164 which are now stabilized by a cation-π interaction (dashed line). (B) The heteroatoms of the intermediate are involved in multiple binding interactions with the active site functional groups, with dashed lines showing each interaction and the distances in angstroms listed. The active site mutants produced to examine the role of these functional groups are shown in parentheses. (C) The four-coordinate tetrahedral binding site of zinc with the metal–ligand distances annotatedand the position of the catalytic E178 shown.