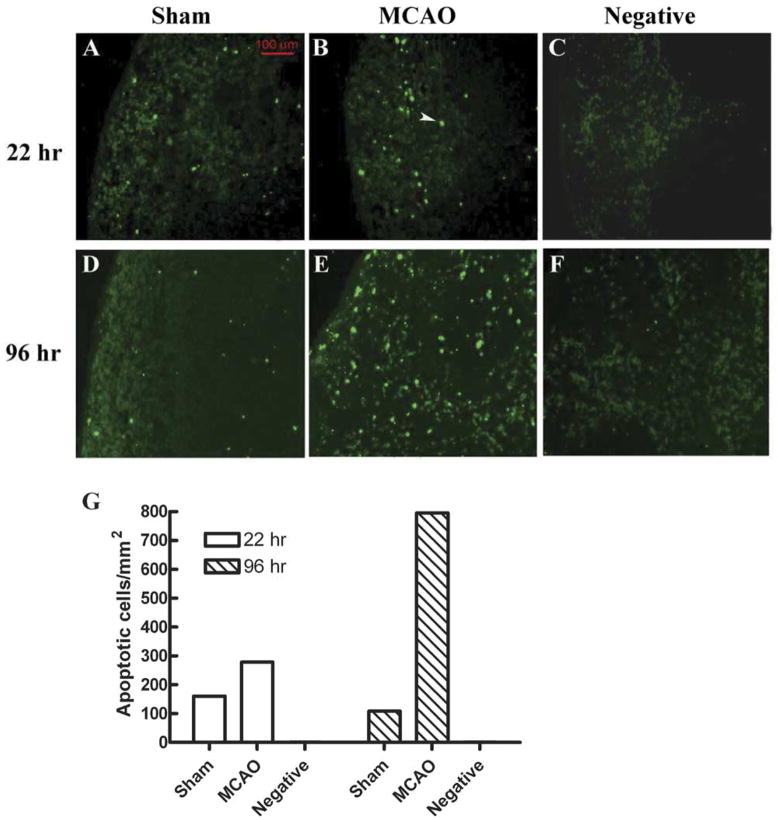
Fig. 2.
(Previously published, Journal of Immunology 176:6523, 2006.) In situ TUNEL assay showed more apoptotic cells in MCAO than in Sham mouse at 22 h and 96 h. (A, B, D, E) Fluorescence microscopic detection of apoptotic cells in mouse splenic tissues from Sham (A, D) or MCAO (B, E) mice, or in a section that was not treated with TdT enzyme ((C, F) negative control). (G) Quantification of the TUNEL-positive cell density in different splenic sections. Splenic tissue sections were prepared and assayed with In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit, Fluorescein (Roche). One section from an MCAO mouse was treated with the same kit but not incubated with TdT enzyme in the labeling step, to serve as negative control. The section was viewed under a fluorescence microscope equipped with a digital camera. Apoptotic cells intensely stained (green) by the TUNEL treatment were counted and their densities were calculated by dividing the total number of apoptotic cells by the total area of the splenic section. A typical apoptotic cell is indicated by the white arrow.