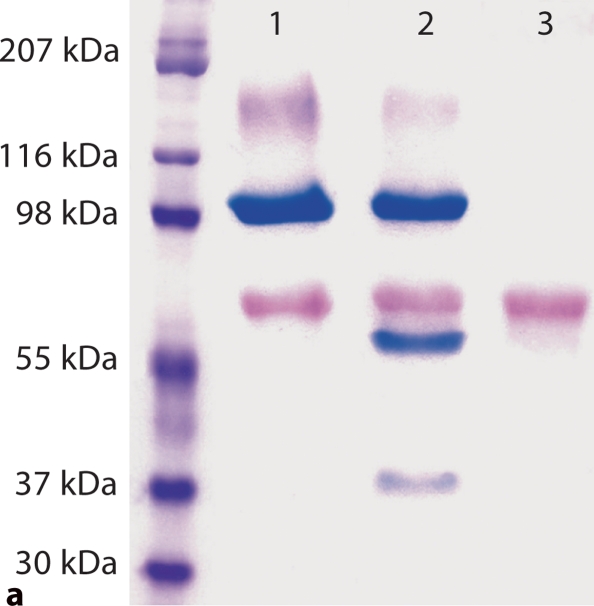
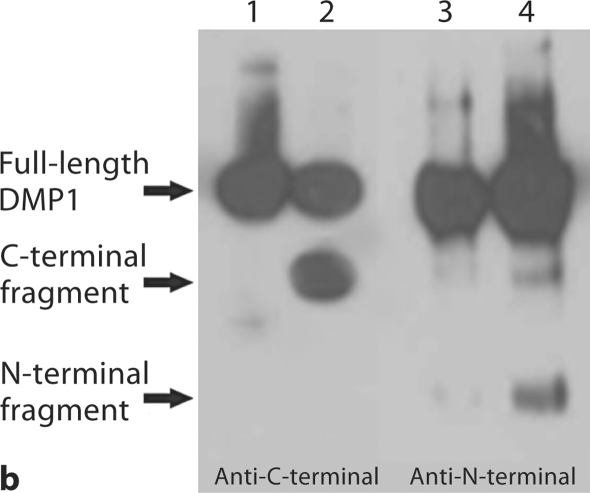
Fig. 1.
Substitution of a single amino acid residue prevented cleavage of mouse DMP1. a Stains-All staining. Lane 1: conditioned culture medium of cells transfected with pcDNA3.1 construct carrying a mouse DMP1 cDNA that encodes DMP1 protein, in which Asp197, an amino acid residue at a key cleavage site, was substituted by Ala197 (note the absence of the lower molecular weight, blue-stained band). Lane 2: pcDNA3.1 vector carrying normal mouse DMP1 cDNA (note the presence of low molecular weight bands stained blue). Lane 3: empty pcDNA3.1 vector (without DMP1 cDNA). The blue band at approximately 100–110 kDa is full-length DMP1. Blue bands at approximately 57 and 37 kDa are DMP1 fragments. Note that the 37-kDa fragment did not stain as darkly as the 57-kDa fragment, which is most likely due to the less acidic properties of the 37-kDa fragment. The purple band at approximately 65 kDa represents BSA from the culture medium. For each lane, 600 μl of lyophilized cell-conditional culture medium was loaded onto SDS-PAGE gels. b Western immunoblotting using polyclonal antibodies against COOH-terminal region of DMP1 (left 2 lanes, anti-DMP1-C-785) and NH2-terminal region of DMP1 (right 2 lanes, anti-DMP1-N-784). Lanes 1 and 3 are the same sample (D197A) as in lane 1 of a; lanes 2 and 4 are the same as in lane 2 of a (DMP1 without mutation). Note the absence of the DMP1 fragments in the lanes with an amino acid substitution at the proposed cleavage site (lanes 1 and 3). For each lane, 300 μl of lyophilized cell-conditioned culture medium was loaded onto SDS-PAGE gels. Please note that DMP1-PG was hardly recognized by the polyclonal antibody against the NH2-terminal region of DMP1.