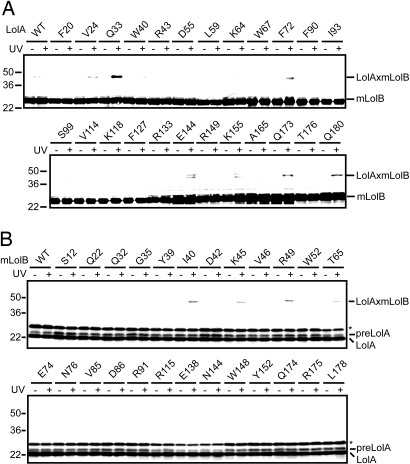
Fig. 2.
In vivo photo-cross-linking between LolA and mLolB. (A) Cells expressing mLolB-His6 and LolA-FLAG derivatives having pBPA in place of the indicated residues were UV-irradiated for 5 min or not irradiated, and then analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-LolB antibodies, as described in Materials and Methods. As a control, cells expressing mLolB-His6 and wild-type (WT) LolA-FLAG were also examined. The cross-linked products generated from LolA and mLolB (LolAxmLolB) are indicated. LolA derivatives containing pBPA at positions 144 and 155 gave 2 cross-linked bands. The upper bands reacted with both anti-LolB and -LolA antibodies whereas the lower ones reacted only with anti-LolB antibodies. The properties of these materials are unknown at present. (B) Cells expressing LolA-FLAG and mLolB-His6 derivatives having pBPA in place of the indicated residues were irradiated as in (A), and then analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-LolA antibodies. As a control, cells expressing LolA-FLAG and wild-type (WT) mLolB-His6 were also examined. The cross-linked products generated from LolA and mLolB (LolAxmLolB) are indicated. A precursor form of LolA (preLolA) was detected when wild-type LolA-FLAG was expressed from a very efficient plasmid (16). Bands migrating slightly slower than that of preLolA represent nonspecific proteins extensively expressed from the plasmid (indicated by asterisks).