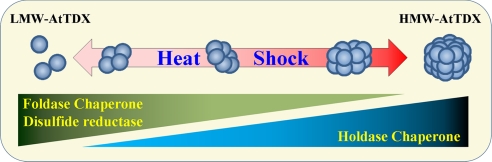
Fig. 6.
A representative model of changes in oligomeric status and function of AtTDX in response to heat shock. When plant cells are exposed to heat shock, LMW AtTDX reversibly change to HMW complexes, in parallel with functional switching from disulfide reductase and foldase chaperone activity to holdase chaperone activity. LMW AtTDX predominantly functions as a disulfide reductase and foldase chaperone, whereas the HMW complex protein acts as a holdase chaperone.