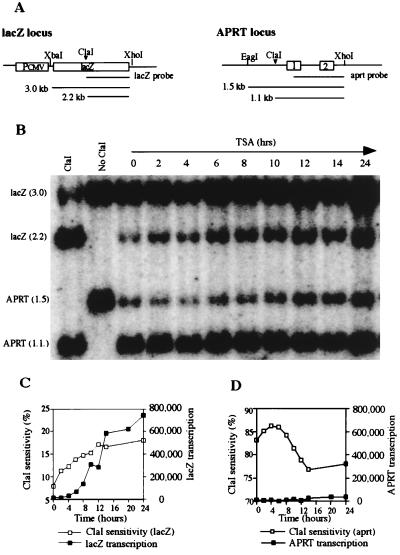
Figure 3.
Endonuclease (ClaI) sensitivity analysis of the transduced lacZ gene and the endogenous APRT housekeeping gene. (A) Partial map of the lacZ gene and endogenous APRT gene illustrating ClaI sites. (B) ClaI sensitivity analysis. Nuclei were isolated from transduced HeLa cells (5 × 105) and were treated with 100 units of ClaI at 37°C for 30 min. Genomic DNA was then isolated and co-digested with EagI, XbaI, and XhoI for Southern blot analysis. TSA treatment for 2 hours increased ClaI sensitivity at the lacZ locus from 7.0% to 11.5%; sensitivity increased to 18% at 24 hours of TSA treatment. The APRT gene was highly sensitive (83%) to ClaI digestion without TSA treatment and remained highly sensitive throughout TSA treatment. (C) Comparison of ClaI sensitivity and transcription of the lacZ gene. ClaI accessibility preceded transcription by at least 4 hours. (D) Comparison of ClaI sensitivity and transcription of the APRT gene. ClaI accessibility of the constitutively expressed APRT gene was high before TSA treatment and remained high after 24 hours of treatment.