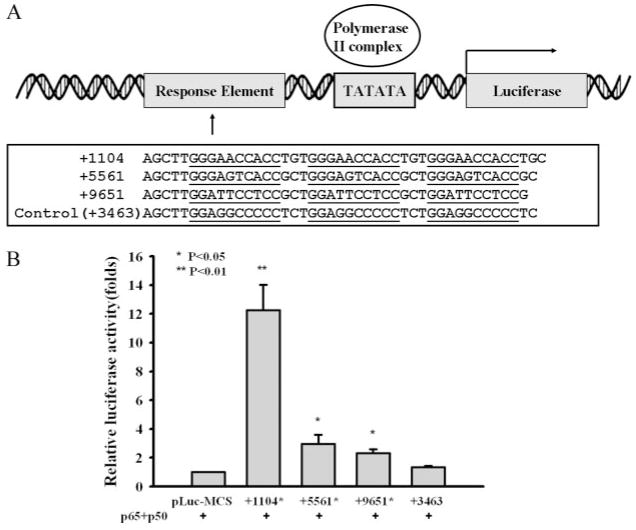
FIGURE 7.
NF-κB binding sequences from FcRn introns can enhance the transcription of the luciferase gene. A, Schematic representation of constructs pLuc-MCS containing NF-κB binding sequences from human FcRn introns 2 and 4. The pLuc-MCS plasmid has the minimal promoter with a TATA box. The plasmids pLuc-MCS +1104, pLuc-MCS +5561, pLuc-MCS +9651, and pLuc-MCS +3463, were constructed as described in Materials and Methods. The NF-κB sequences from FcRn introns are underlined. Numbers represent the locations of NF-κB sites in the human FcRn gene. A DNA sequence corresponding to +3463 in Fig. 4B was used as a negative control. B, HT-29 monolayers were cotransfected with the pLuc-MCS reporter plasmids as indicated and the NF-κB transactivator plasmid p50/65 in addition to the Renilla luciferase pRL-TK control plasmid. The pLuc-MCS backbone serves as a negative control. Luciferase activity was measured 24 h posttransfection. The results represent the mean of three independent experiments.