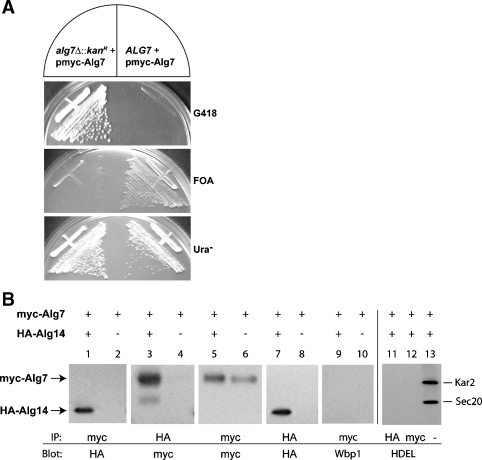
Fig. 2.
Coimmunoprecipitation of Alg7p and Alg14p. (Panel A) Functionality of plasmid-borne myc-ALG7. A viable strain (CNY2) deleted for ALG7 was produced by dissection of an ALG7/alg7Δ::kanR heterozygote that harbored myc-ALG7 on a 2 μ, URA3-containing plasmid (yEp352-GAP-myc-ALG7). The resulting haploid alg7Δ + pmyc-ALG7 strain was streaked on YPAD (+G418), 5′-FOA, and SD (-Ura) plates to assay the functionality of this plasmid-borne ALG7 in a strain in which this is the sole source of Alg7p. (Panel B) Coimmunoprecipitation assays in extracts from strains that express myc-ALG7 (W303 1A + yEpGAP-mycALG7) (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) or that coexpress HA-ALG14 and myc-ALG7 (XGY151 + yEpGAP-mycAlg7) (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9). Detergent extracts were analyzed for coimmunoprecipitation of myc-Alg7p and HA-Alg14 by precipitating myc-Alg7p with the anti-myc antibody, fractionating samples (10 μg) by 12% SDS–PAGE, and detecting HA-Alg14p after immunoblotting with anti-HA antibodies (lane 1), or by precipitating HA-Alg14p with the anti-HA antibody and detecting myc-Alg7p after immunoblotting with the anti-myc antibody (lane 3). The relative amount of myc-Alg7p or HA-Alg14p in the detergent lysates was determined by immunoblotting the precipitate with the same antibody used for the immunoprecipitation (lanes 5–8). Control samples shown in lanes 9, 10, 11, and 12 were loaded on gels directly (lane 13) or subjected to immunoprecipitation with the anti-myc or anti-HA antibody, and blotted with anti-Wbp1 (lanes 9 and 10) or anti-HDEL antiserum (lanes 11, 12, and 13).