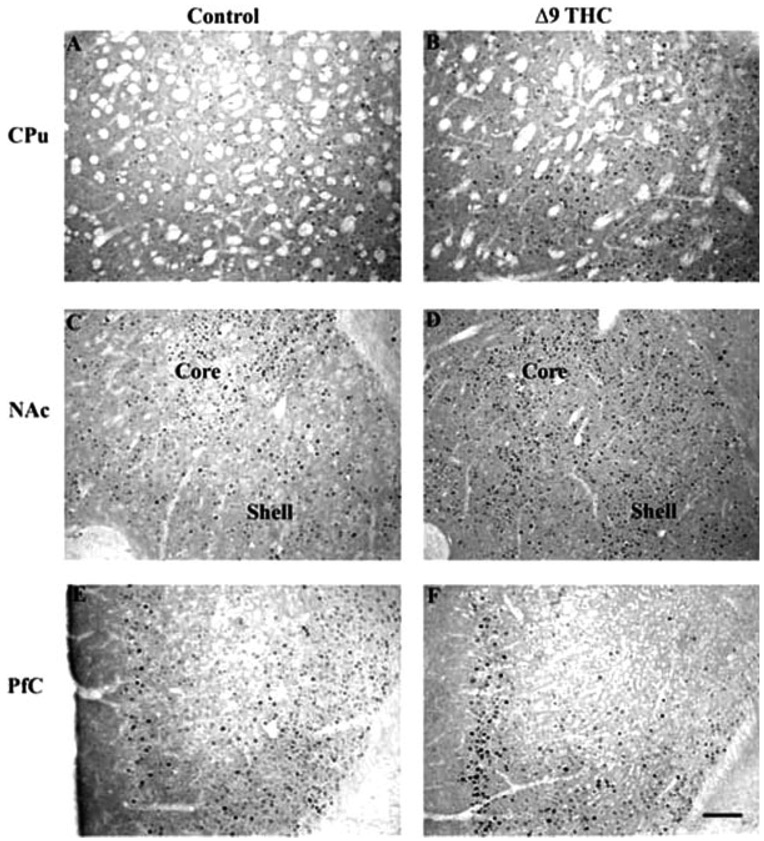
Fig. 4.
Induction of ΔFosB in mouse brain after chronic Δ9-THC treatment. Levels of FosB-like immunoreactivity were analyzed by immunohistochemistry using a pan-FosB antibody in control (A, C, E) and chronic Δ9-THC (B, D, F) animals. Note that chronic Δ9-THC treatment increased FosB-like immunoreactivity in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) core and shell, caudate putamen (CPu; A, B), and prefrontal cortex (PfC; E, F). Note that ΔFosB induction in striatal regions reached statistical significance for NAc core only, despite strong trends in the NAc shell and CPu as shown in the figure (see Fig. 5). Labeling with the C-terminus antibody revealed no positive cells (not shown). Scale bar = 50 µm.