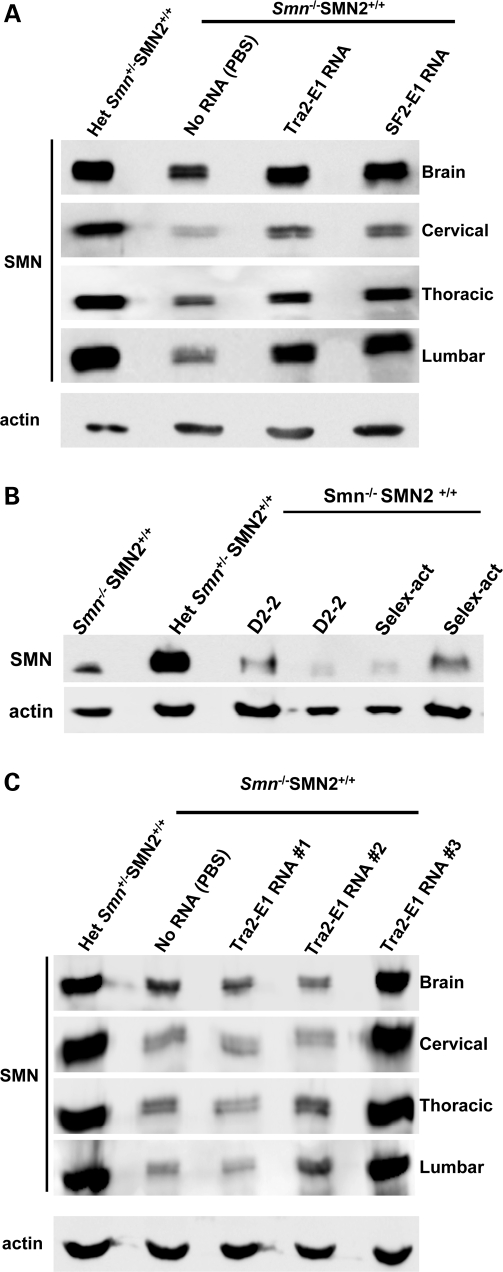
Figure 7.
ICV injection of 2′-O-methyl bifunctional RNAs increases SMN protein levels throughout the CNS. (A) Post-natal day (PND) 2 SMA mice were ICV-injected with 4 µg of the modified bifunctional RNAs, SF2-E1 and Tra2-E1 or PBS. Indicated tissues were isolated 24 h after injections. Western blots were done in quadruplicate, and a representative blot is shown. Multiple mice were injected and tested [Tra2-E1 (n = 13); SF2-E1 (n = 10), data not shown]. (B) Control RNAs do not elevate SMN protein levels. Four micrograms of modified control RNAs were delivered via ICV injection into PND 2 SMA mice and brain tissue was isolated 24 h post-injection. SMN protein levels were observed by western blot, which were done in triplicate, and a representative blot is shown. D2-2 and Selex-act are the two previously described RNAs, corresponding to an SMN intron 7 antisense (D2-2) or three tandem repeats of an in vitro affinity-determined binding motif for hnRNP-A1 (Selex-act). (C) ICV injection of Tra2-E1-modified bifunctional RNA increases SMN protein levels 5 days after a single injection. 2 PND SMA mice were ICV-injected with 4 µg of Tra2-E1 RNA. Five days following injection, the indicated tissues were harvested and SMN western blot performed. Western blots were done in quadruplicate and representative blot is shown.