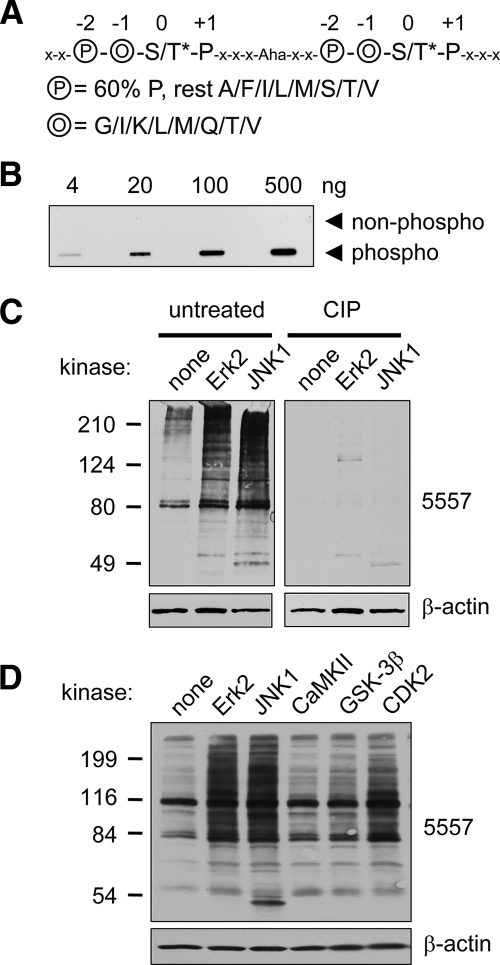
Fig. 1.
Phosphomotif antibody 5557 is phosphospecific and detects MAPK phosphorylation events. A, sequence of phosphopeptide library containing two consecutive consensus MAPK phosphorylation sites used for immunization to produce antibody 5557. The phosphoserine or -threonine (S/T*; 0 position) is followed by proline (1 position) and preceded by two residues, circled O (−1 position; randomly incorporating glycine, isoleucine, lysine, leucine, methionine, glutamine, threonine, or valine) and circled P (−2 position; 60% proline and 40% alanine, phenylalanine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, serine, threonine, or valine). The linker between the two tandem motifs contains five amino acids (x denotes any amino acid except cysteine) and 6-aminohexoic acid (Aha), which was used to increase the distance between the tandem motifs. B, slot blot showing specificity of affinity-purified antibody 5557 for the phosphopeptide library used for immunization versus an identical library of unphosphorylated peptides. C, PSD1 fraction (prepared in the absence of phosphatase inhibitors) was incubated with recombinant active mitogen-activated protein kinases (30 min at 30 °C) as indicated and immunoblotted with antibody 5557. ERK2 and JNK1 strongly enhanced the 5557 phosphoantibody signal (left panel). Treatment of a duplicate membrane with CIP removed the 5557 signal without affecting β-actin. D, PSD1 fraction was incubated with active ERK2, JNK2, CaMKII (with Ca2+ and calmodulin), GSK-3β, or CDK2 (with cyclin A) for 30 min at 30 °C and immunoblotted with antibody 5557.