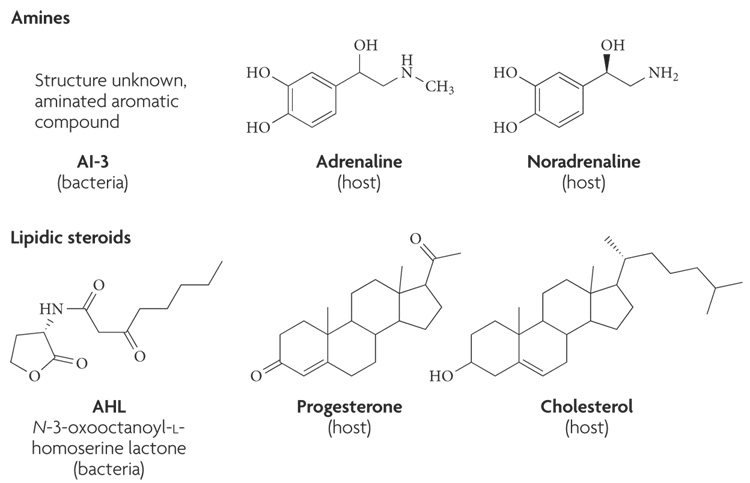
Figure 1. Chemical structures of bacterial and host signals.
The bacterial signal autoinducer (AI)-3 is an aromatic aminated signal; its final structure is still unknown. Because AI-3 is, to a certain degree, hydrophobic, it is not thought to be able to cross the cell membrane. The bacterial signal acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) is composed of a conserved homoserine ring and a variable acyl chain, and usually can cross the cell membrane. The host hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline are cathecolamines that are synthesized from tyrosine and usually do not cross the cell membrane. The host signals progesterone and cholesterol are two examples of lipid host hormones that can cross the cell membrane and bind intracellular receptors.