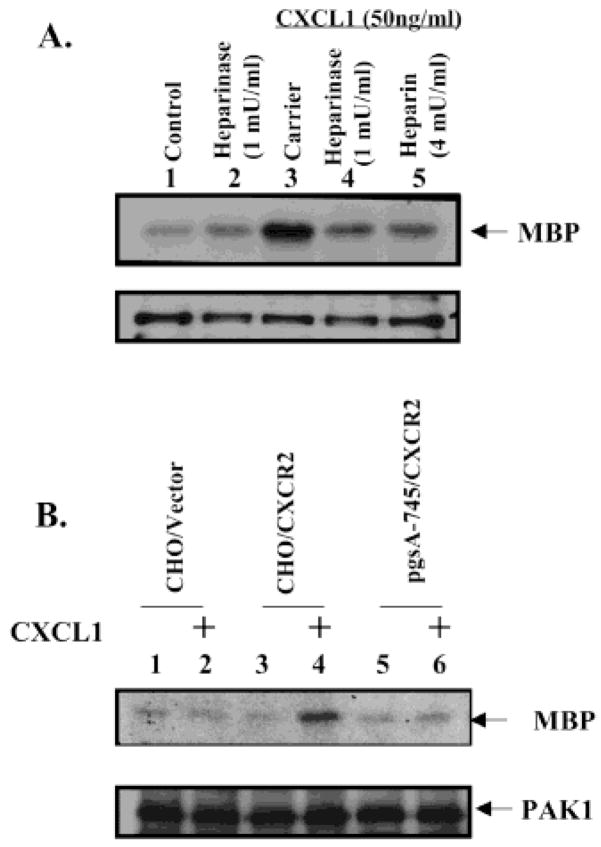
Figure 3.
Cell surface heparan sulfate is required for CXCL1-induced PAK1 activation. (A) Depletion of heparan sulfate by heparinase blocks CXCL-induced PAK1 activation in CXCR2-expressing HEK293 cells. The CXCR2-expressing HEK293 cells were treated with heparinase as in Figure 2A before the stimulation with CXCL1 for 10 min. PAK1 kinase assays were performed as described in Experimental Procedures. Endogenous PAK1 activity was determined by an amount of MBP phosphorylation (top panel). The blot was reprobed with PAK1 antibody to monitor equal loading of PAK1 (lower panel). This figure is representative of three different experiments with similar results. (B) Absence of heparan sulfate in HSPG-deficient CHO cells inhibits CXCL1-induced PAK1 activation. CXCR2-expressing wild-type and HSPG-deficient CHO cells were either untreated or treated with 50 ng/mL CXCL1 for the 10 min after serum starvation for 14 h. PAK1 kinase assays were performed as in panel A. This figure is representative of three different experiments with similar results.