TABLE 3.
Effects of study interventions on changes in body composition, fat distribution, and aerobic fitness1
| CR only (n = 29) | CR + moderate-intensity (n = 36) | CR + vigorous-intensity (n = 30) | P2 | |
| ΔBody weight (kg) | −11.8 ± 4.1 | −12.2 ± 4.5 | −12.3 ± 4.9 | 0.92 |
| ΔTotal fat mass (kg) | −7.4 ± 2.8 | −8.2 ± 3.2 | −8.5 ± 3.8 | 0.45 |
| ΔTotal lean mass (kg) | −4.1 ± 1.9 | −3.4 ± 2.0 | −3.3 ± 1.7 | 0.17 |
| ΔPercentage of body fat (%) | −3.3 ± 2.0 | −4.1 ± 2.2 | −4.3 ± 2.2 | 0.16 |
ΔRelative 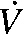 O2max (mL · kg bw−1 · min−1) O2max (mL · kg bw−1 · min−1) |
2.0 ± 2.6 | 2.5 ± 2.6 | 4.1 ± 3.73 | 0.03 |
ΔAbsolute 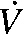 O2max (mL/min) O2max (mL/min) |
−71 ± 255 | −8 ± 213 | 68 ± 252 | 0.10 |
| ΔWaist circumference (cm) | −8.9 ± 3.9 | −9.3 ± 5.0 | −9.9 ± 4.6 | 0.67 |
| ΔHip circumference (cm) | −8.5 ± 4.6 | −10.1 ± 4.6 | −9.4 ± 3.8 | 0.35 |
| ΔWHR | −0.016 ± 0.039 | −0.011 ± 0.044 | −0.020 ± 0.038 | 0.68 |
| ΔAbdominal visceral fat (cm3) | −612 ± 338 | −591 ± 340 | −630 ± 298 | 0.90 |
| ΔAbdominal subcutaneous fat (cm3) | −1051 ± 1023 | −1426 ± 764 | −1007 ± 1136 | 0.18 |
| ΔVSF ratio | −0.03 ± 0.08 | −0.02 ± 0.10 | −0.06 ± 0.09 | 0.34 |
All values are means ± SDs. CR, calorie restriction; 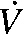 O2max, maximal oxygen uptake; bw, body weight; WHR, waist-hip ratio; VSF, visceral-subcutaneous fat.
O2max, maximal oxygen uptake; bw, body weight; WHR, waist-hip ratio; VSF, visceral-subcutaneous fat.
Decreases within each group for all body composition and fat distribution variables were significant, P < 0.0001 for all, except WHR and VSF, P = 0.003 (paired t test). Increases within each group for relative 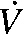 O2max were significant, P < 0.05; changes within group for absolute
O2max were significant, P < 0.05; changes within group for absolute 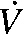 O2max were not significant.
O2max were not significant.
Significantly different from the CR-only and CR + moderate-intensity groups, P < 0.05 (one-factor ANOVA).
