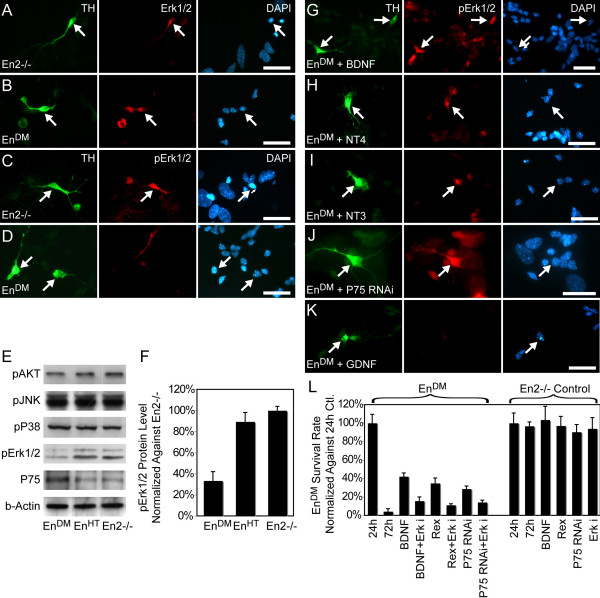
Figure 3.
Differential activation of Erk1/2 in mesDA neurons. (A-D, G-K) Immunohistochemistry of E12 ventral midbrain cell culture stained against TH (green), total Erk1/2 protein (red) (A, B) and phosphorylated Erk1/2 (red) (C-D, G-K). (A-D) While Erk1/2 protein is present in mesDA neurons of both genotypes (A, B), it is only phosphorylated in En2-/- mesDA neurons (C) and not in the En1-/-;En2-/- (EnDM) counterparts (D). (E-I) Erk1/2 becomes activated in EnDM mesDA neurons after treatment with the survival-inducing neurotrophins, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin (NT)4 and NT3, or after silencing of P75NTR (RNA interference (RNAi)) (G-J), but not when glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is applied (I). (E) Western blot of E12 ventral midbrain tissue confirms the immunohistochemical finding of differential phosphorylation between genotypes and shows that neither AKT, part of the phosphotidyl inositol-3 kinase pathway, nor other mitogen-activated protein kinases, such as JNK and P38, are differentially activated. (F) Quantification of phosphorylated Erk1/2 in western blot normalized against En2-/- tissue. (L) Number of TH-positive cells in EnDM and En2-/- ventral midbrain cultures after 72 hours, treated with the 400 nM Mek inhibitor U0126 in conjunction with BDNF, Penetratin-coupled P75NTR double-stranded RNA oligonucleotides and the P75NTR inhibiting antibody (Rex). Numbers are normalized against untreated cultures at 24 hours. The rescue effect is significantly reduced when the EnDM cultures are treated with the Erk1/2 inhibitor. Scale bars: 25 μm. Error bars indicate standard error. Ctl, control.