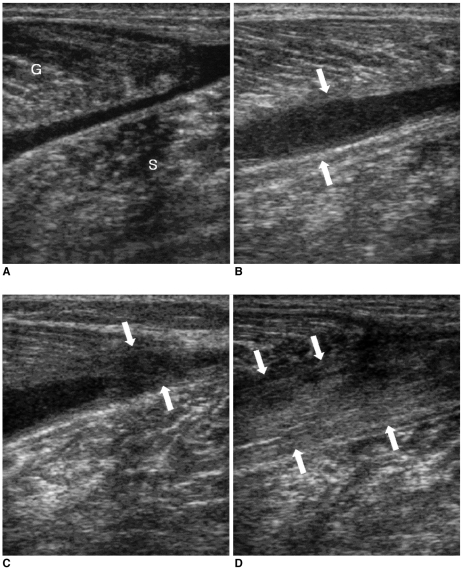
Fig. 2.
A 31-year-old male with complete rupture of the medial head of the gastrocnemius at the musculotendinous junction.
A. The longitudinal US image obtained one day after the injury shows a poorly defined large fluid collection that separates the medial head of the gastrocnemius from the soleus muscle. G = gastrocnemius muscle, S = soleus muscle.
B. The longitudinal US image obtained four weeks later shows union of the hypoechoic tissue between the distal ends of the medial head of the gastrocnemius with the soleus muscle (arrows).
C. The longitudinal US image obtained three months following the injury shows the reparative process (arrows) as a hypoechoic area starting from the periphery of the fluid collection.
D. The longitudinal US image obtained six months following injury shows the healing of the rupture as heterogeneous echogenicity (arrows) that corresponds to fibrous tissue interposed between the medial head of the gastrocnemius and the soleus muscle.