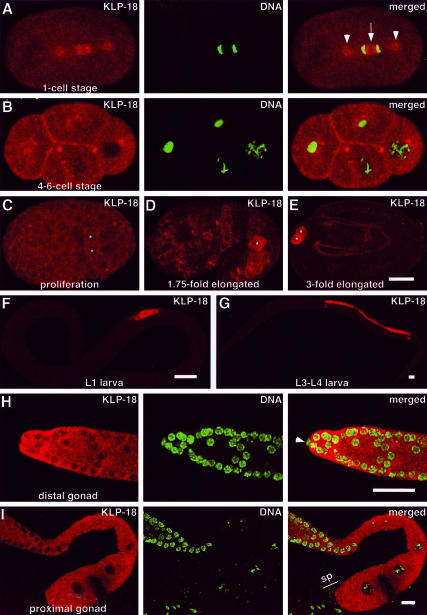
Figure 2.
KLP-18 localization during development. Embryonic (A–E) and postembryonic stages (F–I) were stained for KLP-18 (red) and DNA (Yoyo-1, green; in A, B, H, and I). Anterior is to the left. (A) During mitotic anaphase KLP-18 is concentrated on the centrosomes (arrowheads) and on the MTs between the separating masses of chromatin, with a dim zone at the spindle equator (arrow). (B) KLP-18 becomes concentrated near plasma membranes at sites of cell-cell contact. (C–E) During later embryo development, KLP-18 signal begins to increase in the germ line precursor cells, Z2 and Z3, which were identified by double staining with anti-PGL-1 antibodies (Kawasaki et al., 1998; our unpublished data) and are marked with asterisks. (F and G) KLP-18 accumulates in the germ line throughout larval development. (H and I) KLP-18 is present in the adult germ line. The gonad distal tip cell, which is somatic (arrow-head in H), and mature sperm (“sp” in I) do not contain detectable KLP-18. Bars, 10 μm.