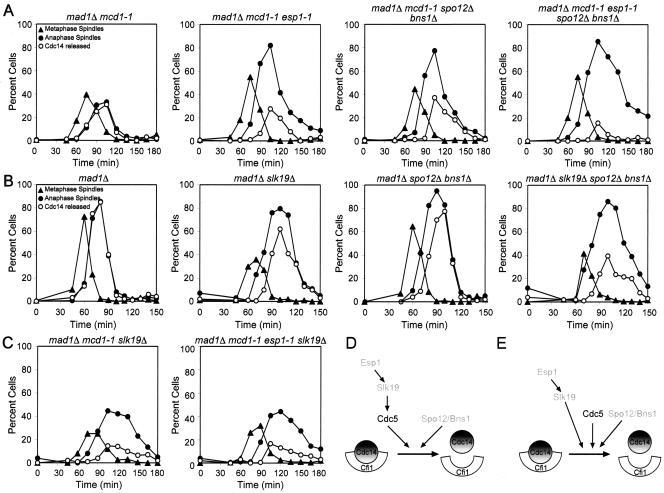
Figure 3.
SPO12 and BNS1 function in parallel to ESP1 and SLK19. (A) mad1Δ mcd1-1 (A2784), mad1Δ mcd1-1 esp1-1 (A3550), mad1Δ mcd1-1 spo12Δ bns1Δ (A8129), and mad1Δ mcd1-1 esp1-1 spo12Δ bns1Δ (A8130) cells carrying a CDC14-3HA fusion were arrested in G1 in YEPD medium with α-factor (5 μg/ml) and subsequently released into YEPD lacking pheromone at 37°C. α-Factor was readded 90 min after release to prevent entry into a subsequent cell cycle. The percentage of cells with metaphase spindles (closed triangles), anaphase/telophase spindles (closed circles) as well as the percentage of cells with Cdc14-HA released from the nucleolus (open circles) was determined at the indicated times. (B) mad1Δ (A2853), mad1Δ slk19Δ (A4302), mad1Δ spo12Δ bns1Δ (A5408), and mad1Δ spo12Δ bns1Δ slk19Δ (A5515) cells all carrying a CDC14-3HA fusion were arrested in G1 in YEPD medium with α-factor (5 μg/ml) and subsequently released in a synchronous manner into YEPD lacking pheromone at 25°C. α-Factor pheromone was readded 80 min after release to prevent entry into a subsequent cell-cycle. Cells were analyzed as described in (A). (C) mad1Δ mcd1-1 slk19Δ (A8132) and mad1Δ mcd1-1 esp1-1 slk19Δ (A8132) cells carrying a CDC14-3HA grown and analyzed as described in A. (D and E) Possible order of function of FEAR network components. SLK19 functions downstream of ESP1 (D, E). SPO12 and BNS1 function in parallel to ESP1, SLK19, and CDC5 (D and E). CDC5 could function in either of two ways in the FEAR network. CDC5 could act downstream of ESP1 and SLK19 (D) or in parallel to the two genes (E).