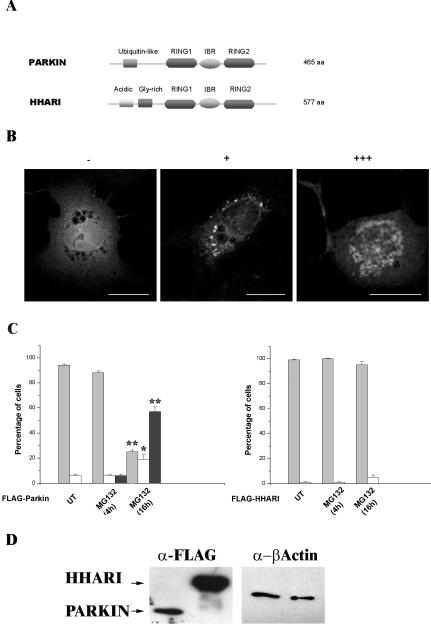
Figure 3.
Inclusion body formation by Parkin is not a general response of RING-IBR-RING proteins to proteasome inhibition. (A) Schematic illustrating the domain structures of Parkin and HHARI. Parkin and HHARI demonstrate structural homology at the 3′ C-terminus. (B) COS-7 cells transfected with the FLAG-Parkin construct, stained with anti-FLAG antibodies as described for Figure 1. Cells were scored as either containing no inclusions (-), small individual inclusions (+), or large inclusions (+++). Bars, 20 μm. (C) COS-7 cells were transfected with FLAG-Parkin (left) or FLAG-HHARI (right). MG132 (20 μM) was added to cells for 4 or 16 h before fixation. The presence of Parkin or HHARI was assessed by immunofluorescence using the anti-FLAG antibody as described for Figure 1. Light gray bars, -; white bars, +; and dark gray bars, +++. Error bars indicate the SE from the mean. The asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference between the percentage of untreated cells with or without inclusions vs. the numbers of MG132-treated cells at each time point. *p < 0.005; ** p < 0.001. N-Terminal Myc-tagged and pDsRed1-C1 Parkin or HHARI constructs produced similar results. (D) Lack of HHARI inclusions is not due to poor expression of the construct. COS-7 cells were transfected with FLAG-Parkin or FLAG-HHARI. Forty-four hours post-transfection, cell lysates were prepared in Triton X-100 buffer. Ten micrograms of each soluble fraction was separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG and anti-β-actin antibodies. Arrows indicate the presence of the respective FLAG construct.