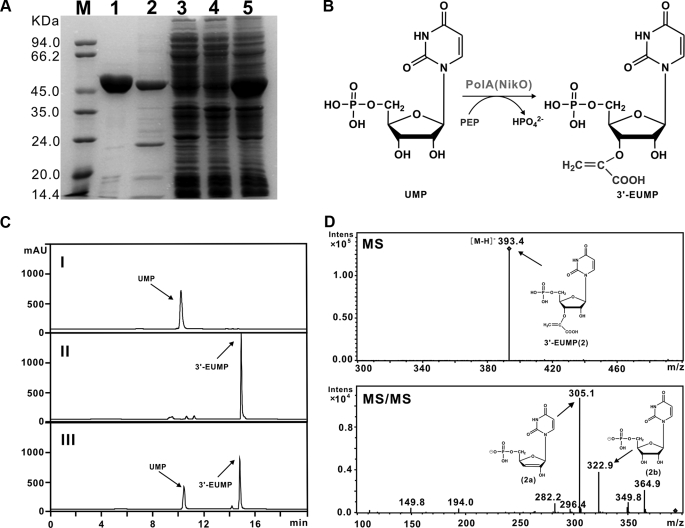
FIGURE 5.
Characterization of PolA as an enolpyruvyltransferase. A, SDS-PAGE analysis of PolA and NikO proteins. Purified His6-tagged NikO (lane 1), PolA (lane 2), soluble proteins of cell-free extract from E. coli BL21 (DE3)/pLysE/polA before (lane 4) and after (lane 3) induction with IPTG, and total proteins of cell-free extract of E. coli BL21 (DE3)/pLysE/polA after induction with IPTG (lane 5), were aligned with molecular mass markers (M). B, conversion mechanism of UMP to 3′-EUMP catalyzed by PolA. C, HPLC analysis of the products catalyzed by PolA (III) and NikO (II), respectively. UMP (I) is included as a negative control. D, MS/MS fragmentation of the products 3′-EUMP catalyzed by PolA in negative mode.