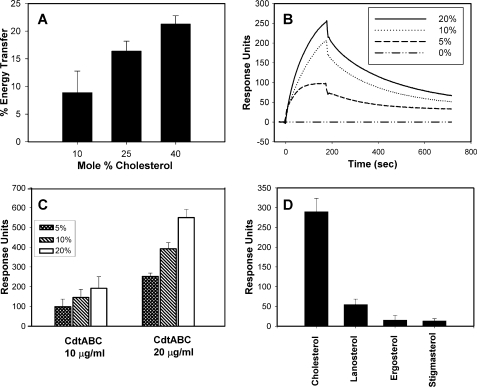
FIGURE 2.
Cdt holotoxin preferentially binds to LUVs containing cholesterol. The interaction of Cdt holotoxin with LUVs containing varying amounts of cholesterol was analyzed by FRET and SPR. Panel A shows FRET analysis of Cdt with LUVs containing varying amounts (10–40 mol %) cholesterol. Values are the mean ± S.D. (n = 3), expressed as relative % energy transfer. Results are statistically significant (p < 0.05; multivariant analysis of variance with post-hoc Scheffe test) for differences in energy transfer as cholesterol concentration is increased. Panel B shows the SPR results of Cdt interaction with LUVs. An overlay of sensorgrams shows the interaction of Cdt (10 μg/ml) with immobilized LUVs containing decreasing concentrations of cholesterol; data points were collected every 0.2 s. Data are plotted as response units versus time and are representative of three experiments. Panel C shows the results of SPR analysis for the interaction of two concentrations of Cdt (10 and 20 μg/ml) with immobilized LUVs containing 5, 10, and 20% cholesterol; data are the mean ± S.D. of three experiments and are plotted as the number of response units obtained from each sensorgram after 3 min post-injection. Results are statistically significant (p < 0.29; multivariant analysis of variance) for differences in response units as toxin concentration is increased. Panel D shows the results of SPR analysis of Cdt (20 μg/ml) with immobilized LUVs containing 20% of either cholesterol, lanosterol, ergosterol, or stigmasterol. The mean ± S.D. of the maximum response is plotted for three experiments. Results are statistically significant for differences between cholesterol and lanosterol (p < 0.001), cholesterol and ergosterol (p = 0.029), and cholesterol and stigmasterol (p = 0.029). To verify that liposomes contained comparable levels of sterol, aliquots of liposomes were extracted, and the amount of sterol was determined as described in Fig. 1; extraction yields were 7.9 μg (lanosterol), 8.6 μg (ergosterol), 7.6 μg (stigmasterol), and 7.8 μg (cholesterol).